これらの AFM プローブ は他のお好きなBudgetSensors AFM プローブ と同時に購入してBudget Combo Boxを作ることができます!
これらの AFM プローブ は他のお好きなBudgetSensors AFM プローブ と同時に購入してBudget Combo Boxを作ることができます!
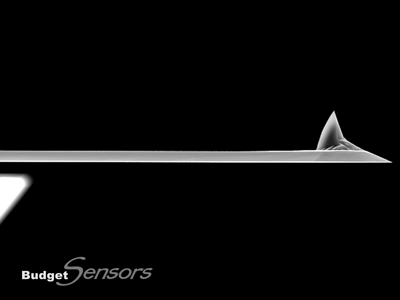
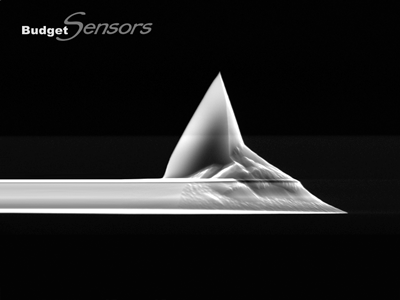
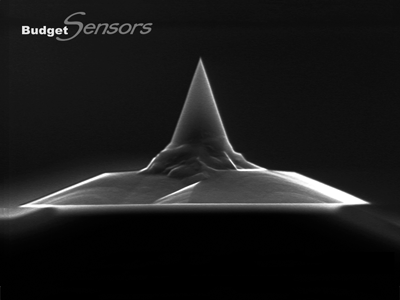
高周波数ノンコンタクトモードタッピングモード用.モノリシックシリコンAFMプローブです。反転ティップにより、高いサンプルに対しても対称性の良いイメージングを可能にします。また安定したサイズのティップ先端により、高分解能と高い繰り返し再現性をご提供します。
AFMホルダーチップはほとんどの市販AFMに取り付けられます。
液中での測定では、背面金コートのTap300GD-Gもしくは全面金コートのTap300GB-Gをご使用ください
高品質かつ低価格のプローブをお客様に!
この製品にはホルダーチップの背面にアライメント溝があります
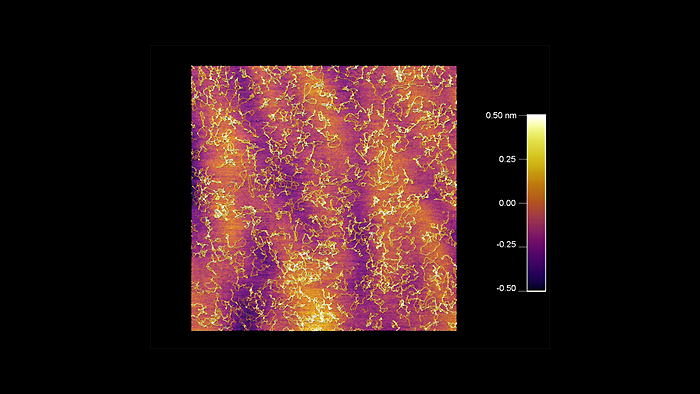
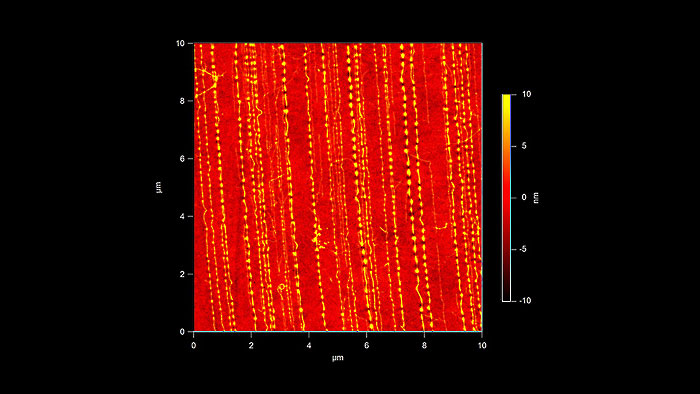
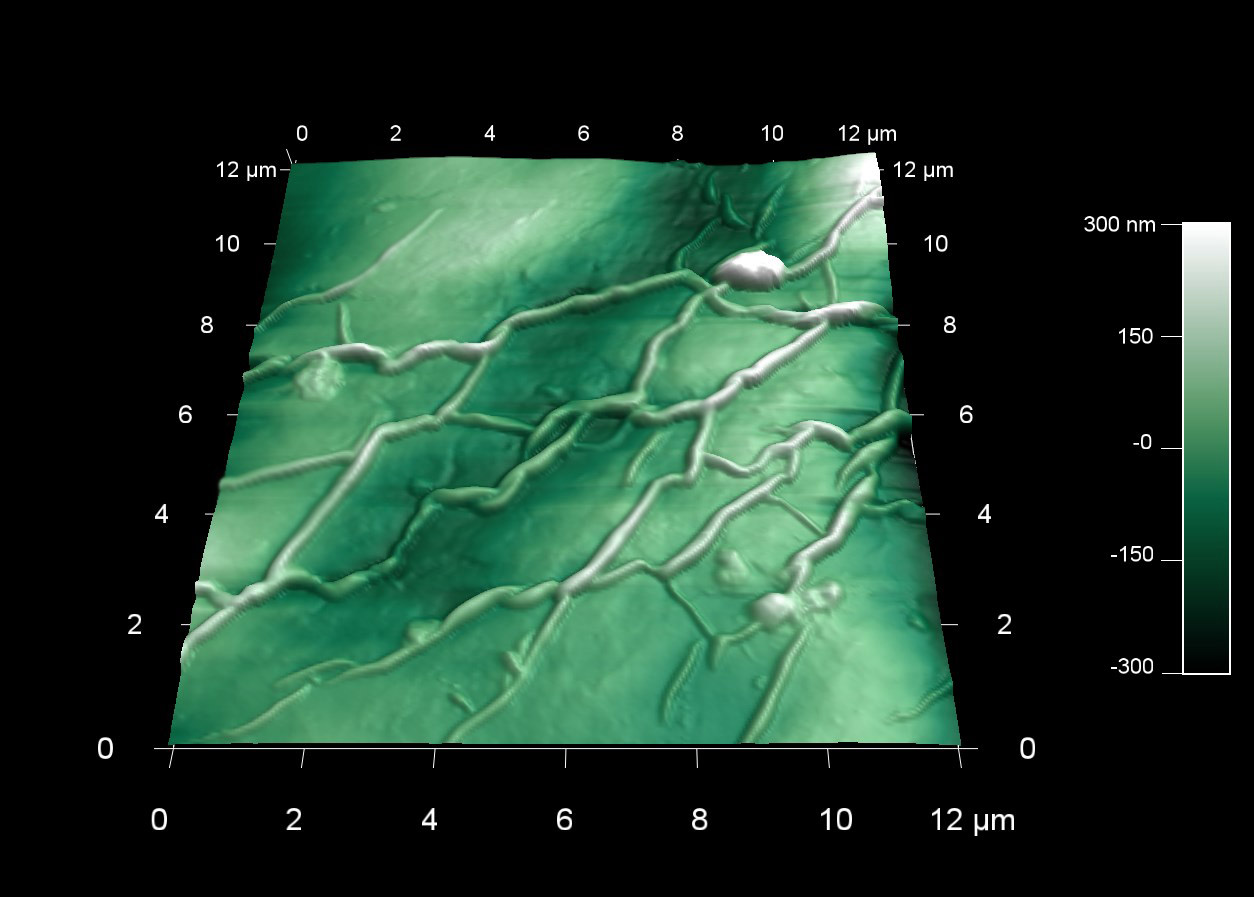
乾燥後のDNAの表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM probe on an Asylum Cypher AFM system, 5 micron scan size
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
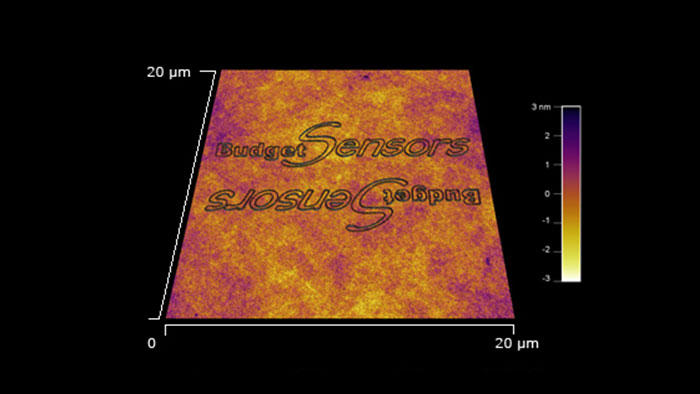
ポリカーボネートにスクラッチリソグラフィで描画したBudgetSensorsロゴ BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G使用AFMはAsylum MFP 3D
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G 20umスキャン Asylum MFP 3D AFM システムで測定
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
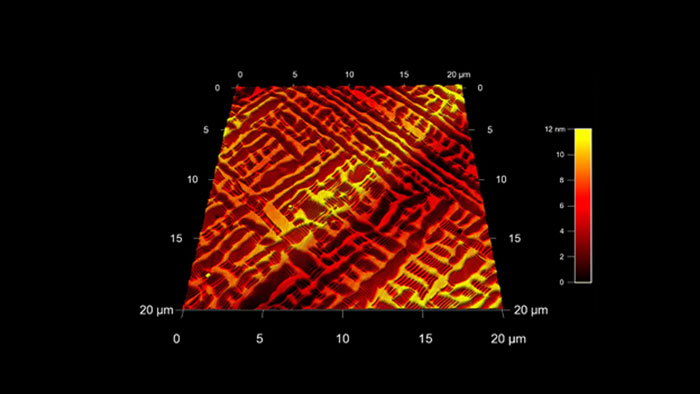
ランタンアルミネート(LAO)上のビスマス系イオンオキサイド薄膜 (BFO)
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G Asylum Cypher AFM システムで測定 20umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
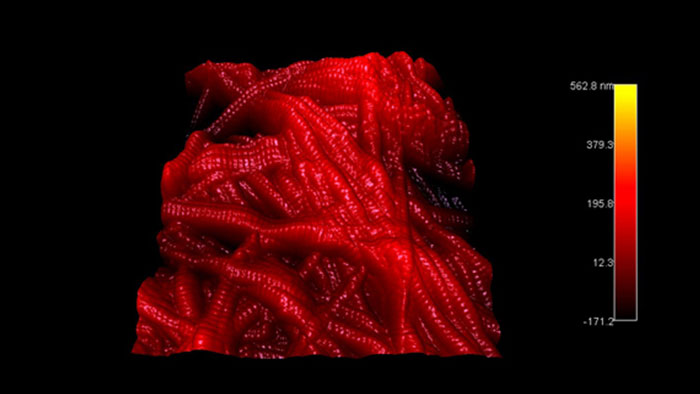
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G 4μmスキャン Tap300Al-Gで測定 Asylum Cypher AFM システム使用
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
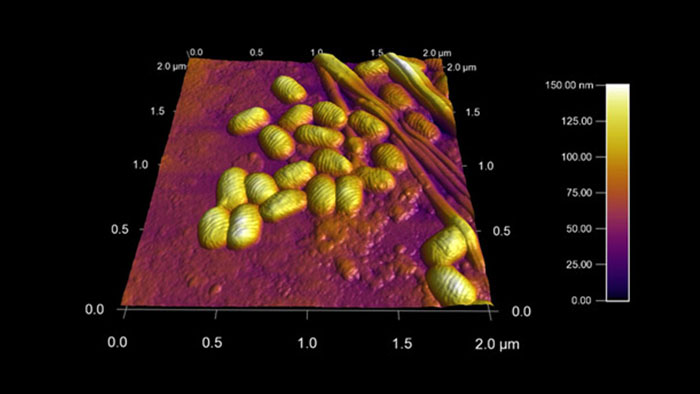
ポックスウイルス
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G Asylum MFP 3D AFMシステムで測定 2umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
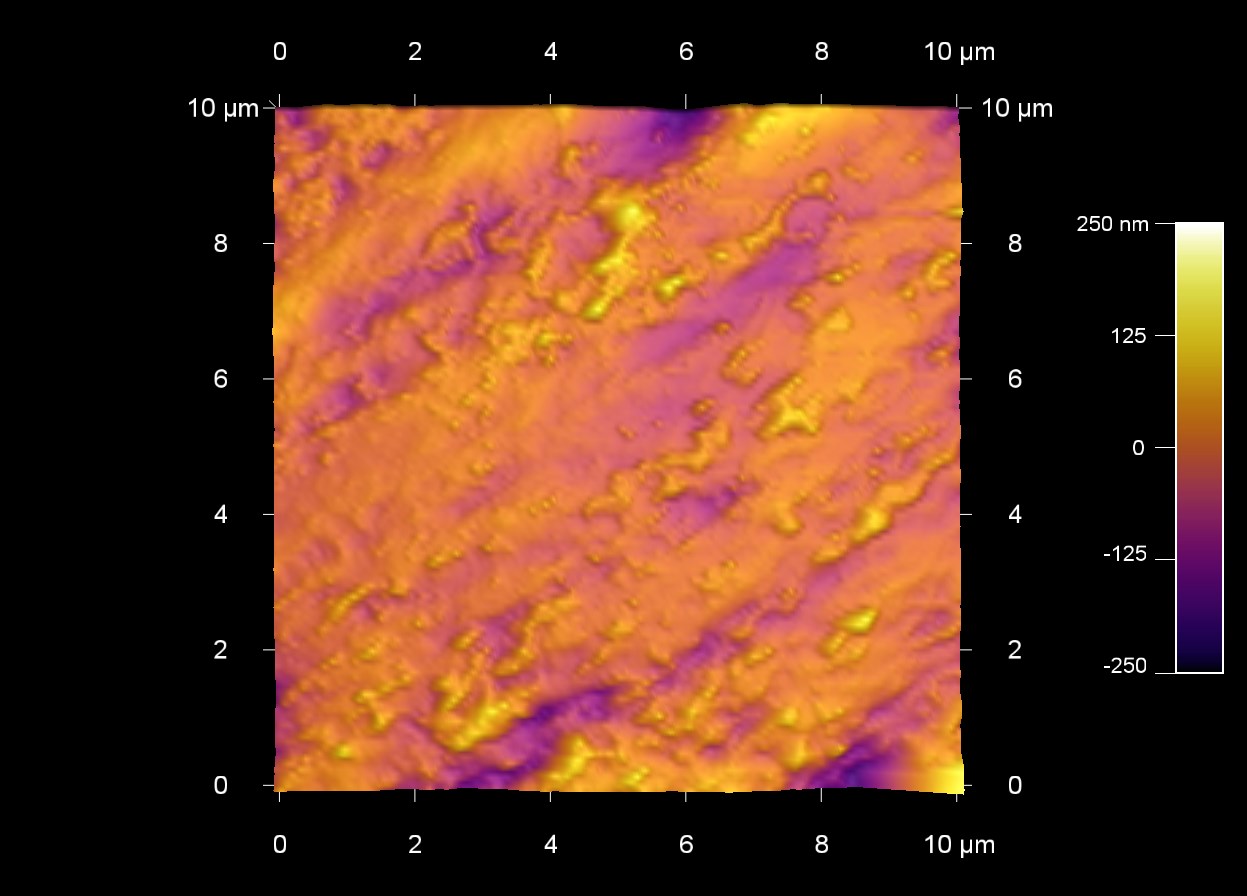
オレンジの皮の表面
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G 10 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
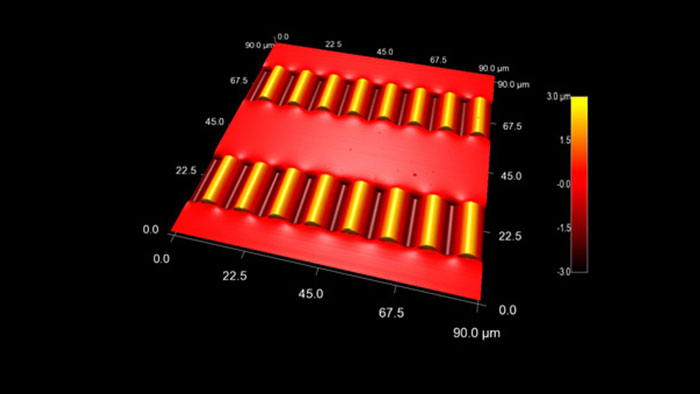
柔軟性のあるPDMS基板上に作られたシリコンナノリボン
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G Asylum MFP-3D AFM システムで測定 90umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
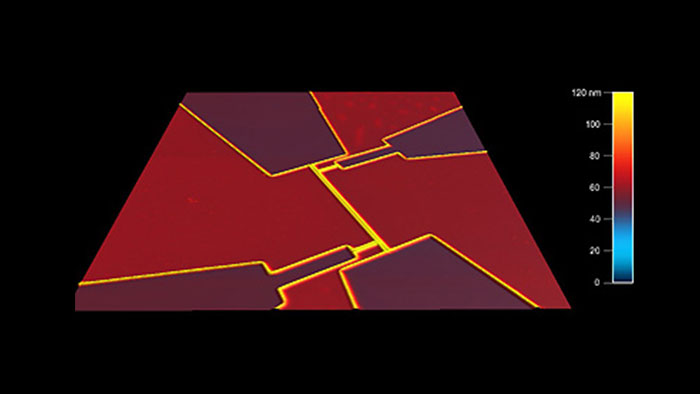
超電導量子フォトンディテクタ
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G Asylum MFP-3D AFMシステムで測定 25umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
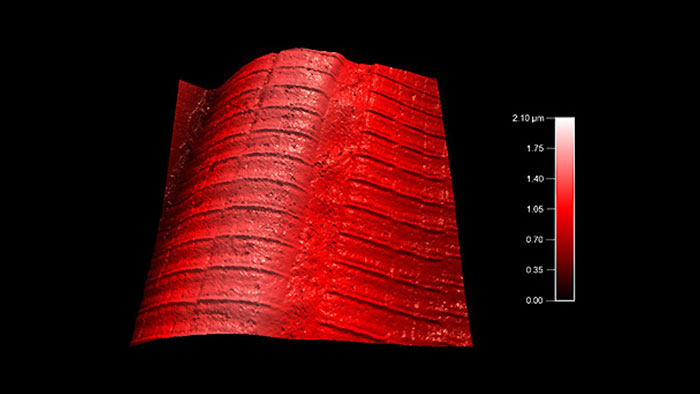
マウスの筋線維
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G Asylum MFP-3D AFM システムで測定 20 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
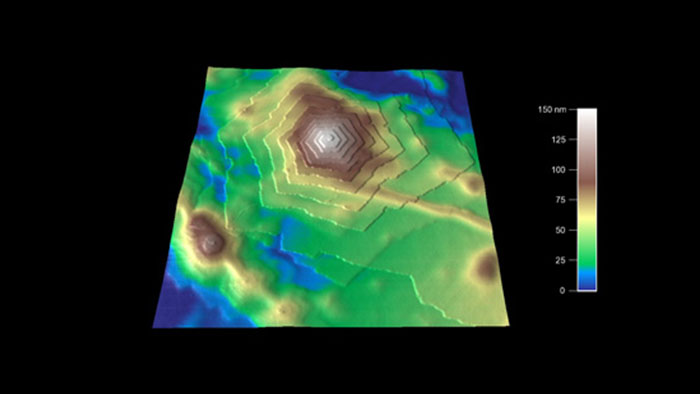
ポリマー表面の結晶構造
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G Asylum MFP-3D AFMシステムで測定 3umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
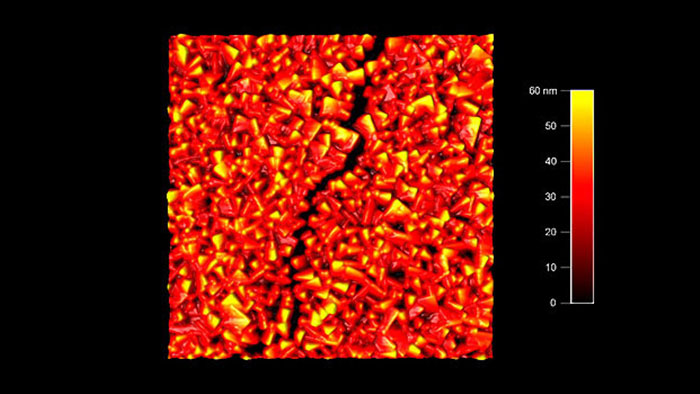
ナイトライド薄膜のクラック
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G Asylum Cypher AFM システムで測定 2umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
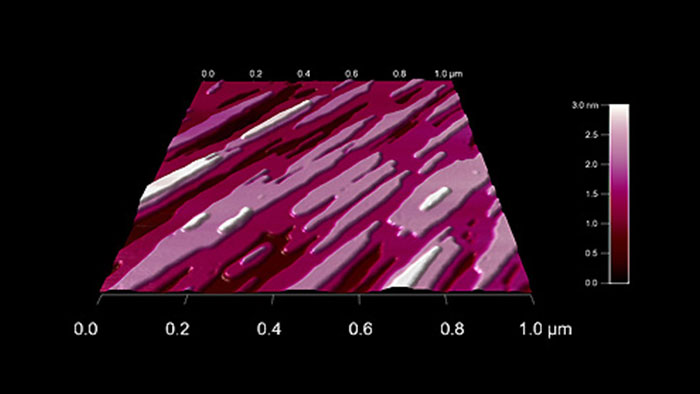
水でエッチングされた石膏の結晶構造
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G Asylum Cypher AFM システムで測定 3umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA

クォーツ上のカーボンナノチューブ バンドル構造とクォーツの原子ステップが見える
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G Asylum Cypher AFM システムで測定 3umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
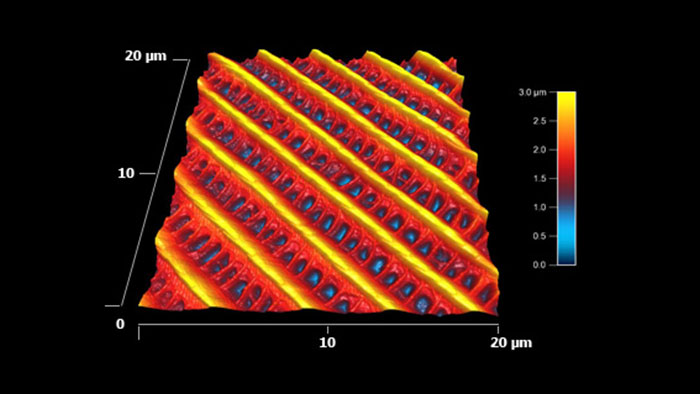
蛾の羽の表面形状 このナノ構造により、羽は疎水性をもち、かつ水に対し方向性を持つ。 水滴は常に体から羽の末端に向かって流れ、体をドライに保つようになっている。
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G Asylum Research MFP-3D AFM システムで測定 20umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
PDMS上のシングルウォールカーボンナノチューブ 水平面方向に圧縮するとナノチューブが波状に変形する
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G 10 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
SEBS ブロックコポリマーの位相イメージ 表面形状を3Dで表示し、位相イメージをカラーデータとして重ね合わせて表示した
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ, 4 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
ゼインタンパク質とコレステロール
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM probe, 15 micron scan size
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
パラジウムの原子ステップ
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ 8umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
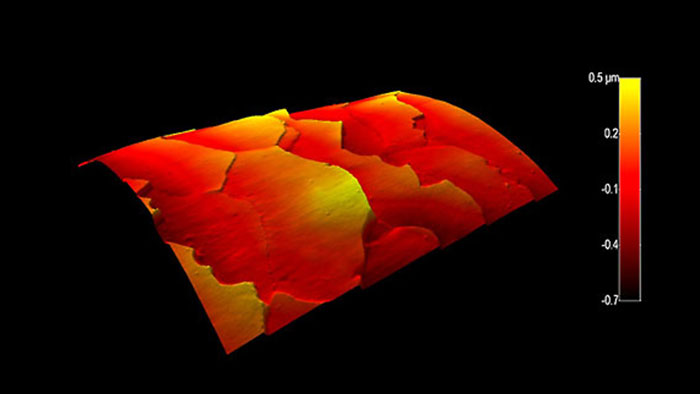
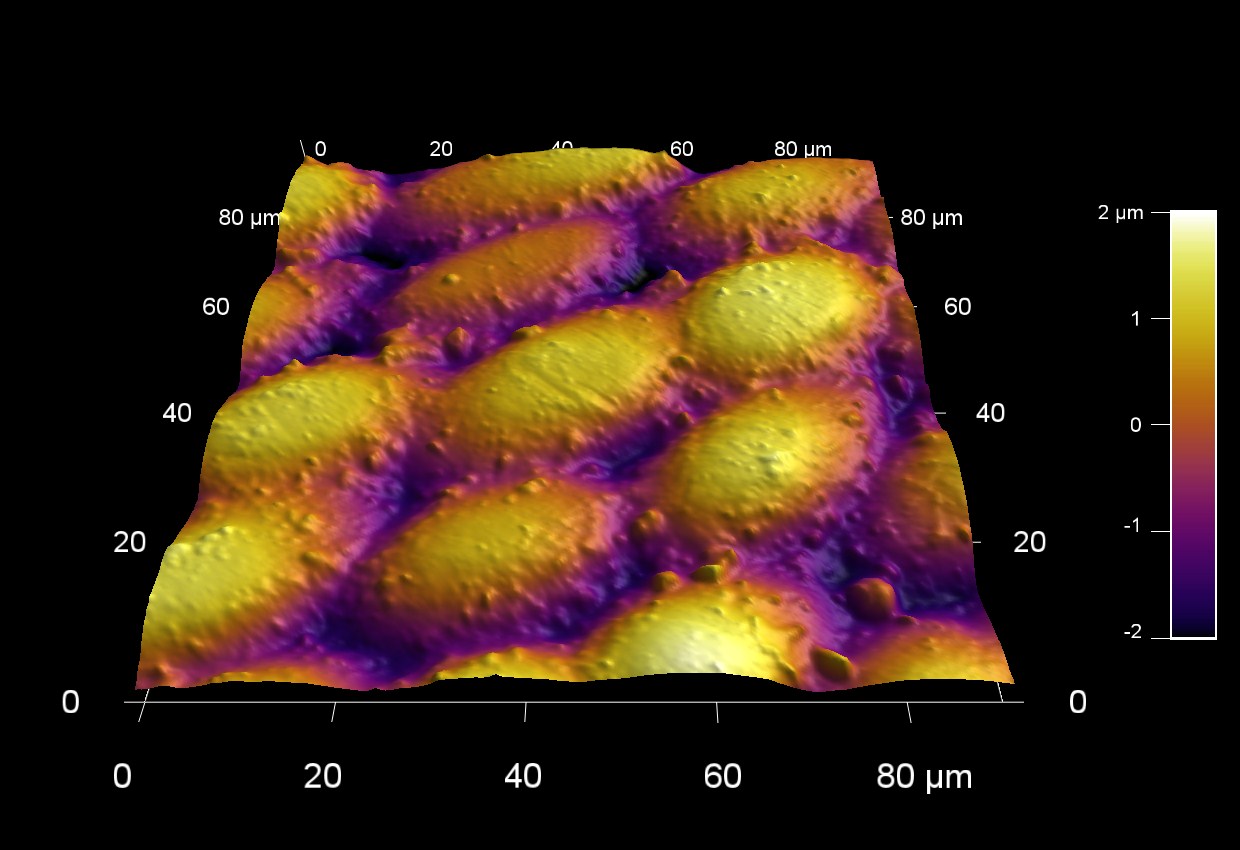
湾曲した人間の毛髪
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM probe, 35 micron scan tsize
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
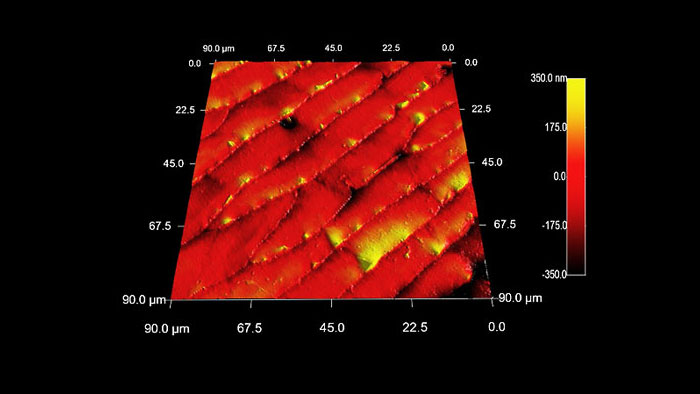
蟻の腹部の表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ 90 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
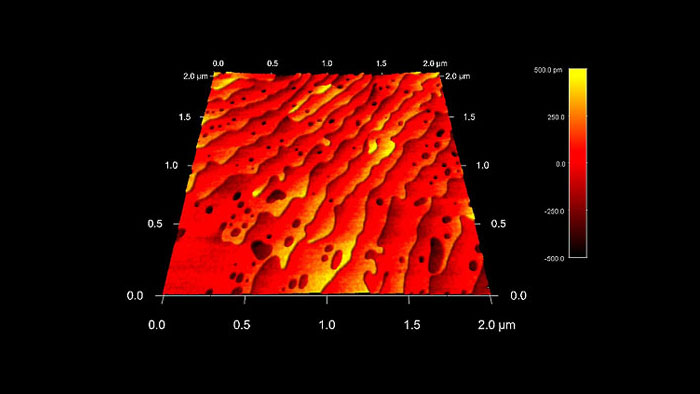
4オングストロームのステップを持つストロンチウムチタン酸化物(SrTiO3)表面
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 2umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
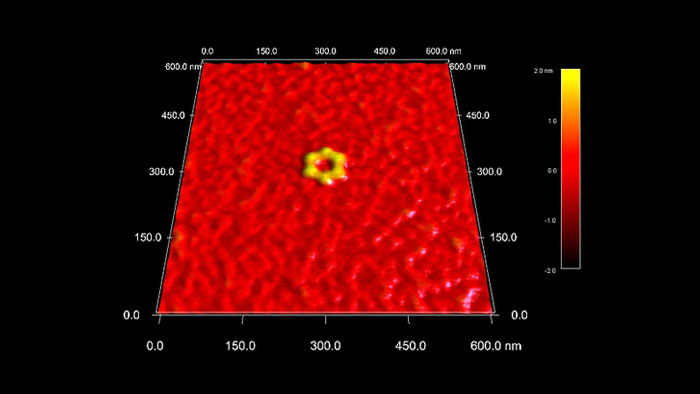
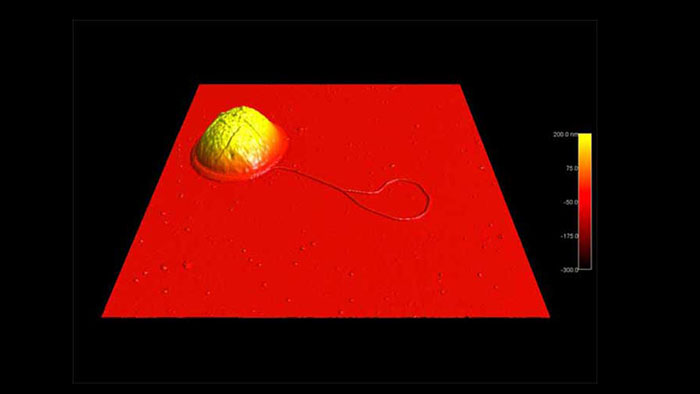
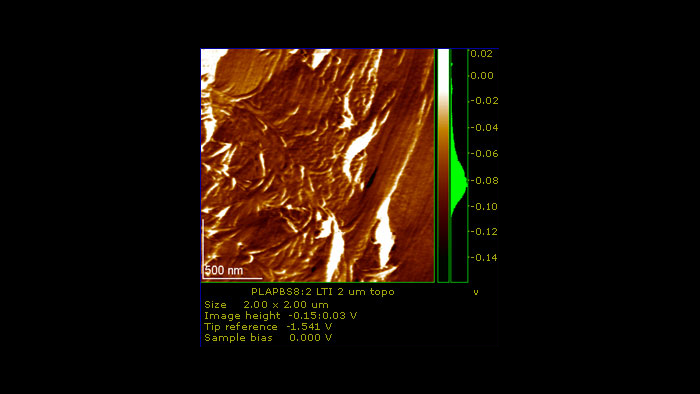
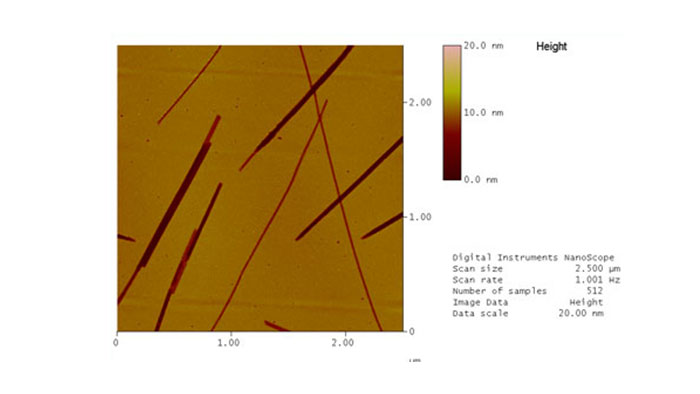
六角形を形成するDNA
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ, 600 nmスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
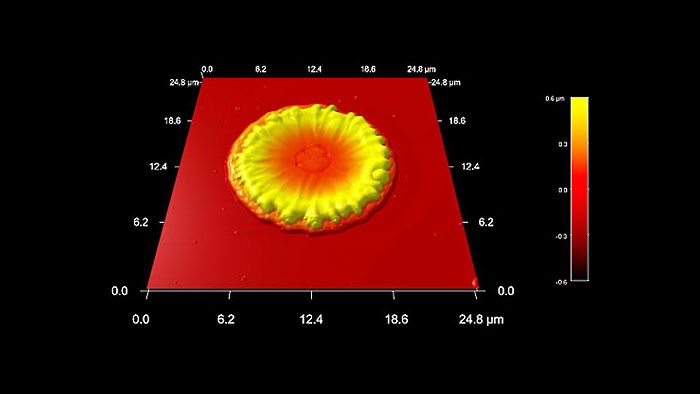
宇宙船のイオンスラスターの排気の溶融銅液滴が衝突したシリコン表面
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM probe, 25 micron scan
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
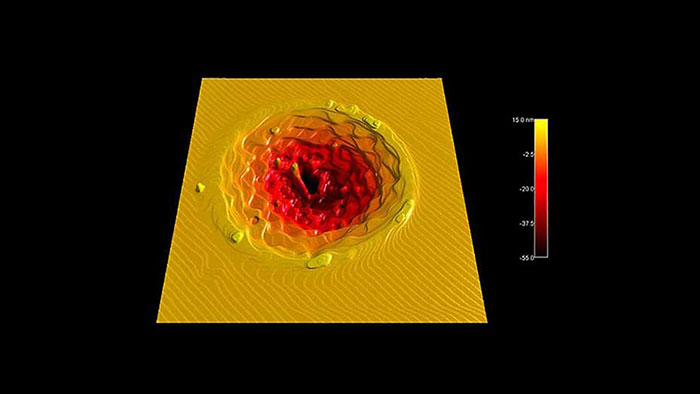
サファイア基板にフェムト秒レーザーパルスを照射し、その後アニールしてステップ構造を形成します。最表面は単一原子ステップ (3 Å) で覆われています。
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ, 20 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
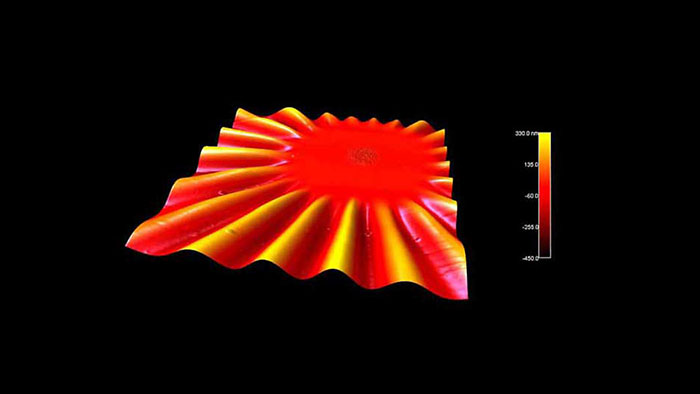
短いレーザーパルスで加熱した後の、ニッケルナノ粒子を含む非常に薄い (30 nm) 自立窒化ケイ素薄膜。ナノ粒子が基板と反応し、膜内に誘発された応力により膜表面に大きな波紋が生じている。
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ 90 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
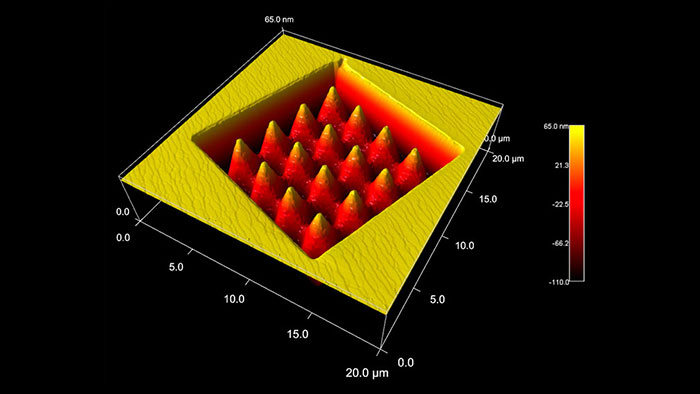
集束イオンビーム (FIB) で削られた酸化マグネシウム (MgO) 結晶。上部の加工されていない表面には、単一および二重の原子ステップが示されています。
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 20 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA

ガラス上のポリ(ベンジル-ベータ-L-グルタミン酸)結晶
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ, 30 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
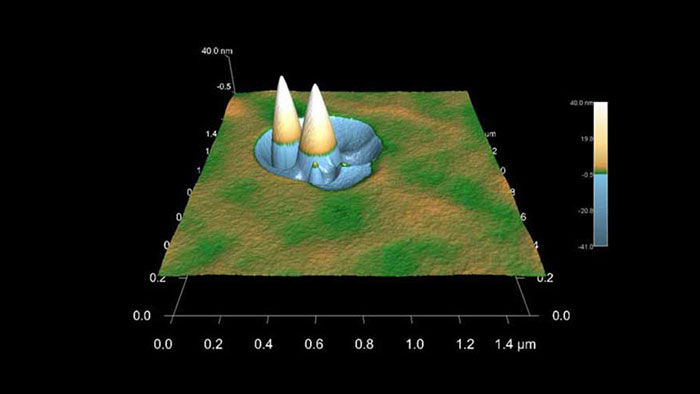
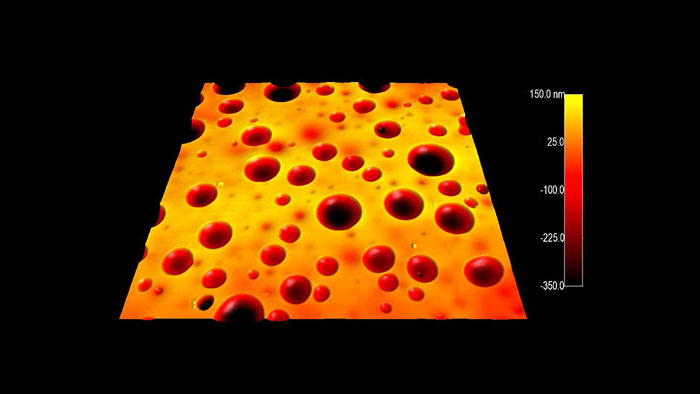
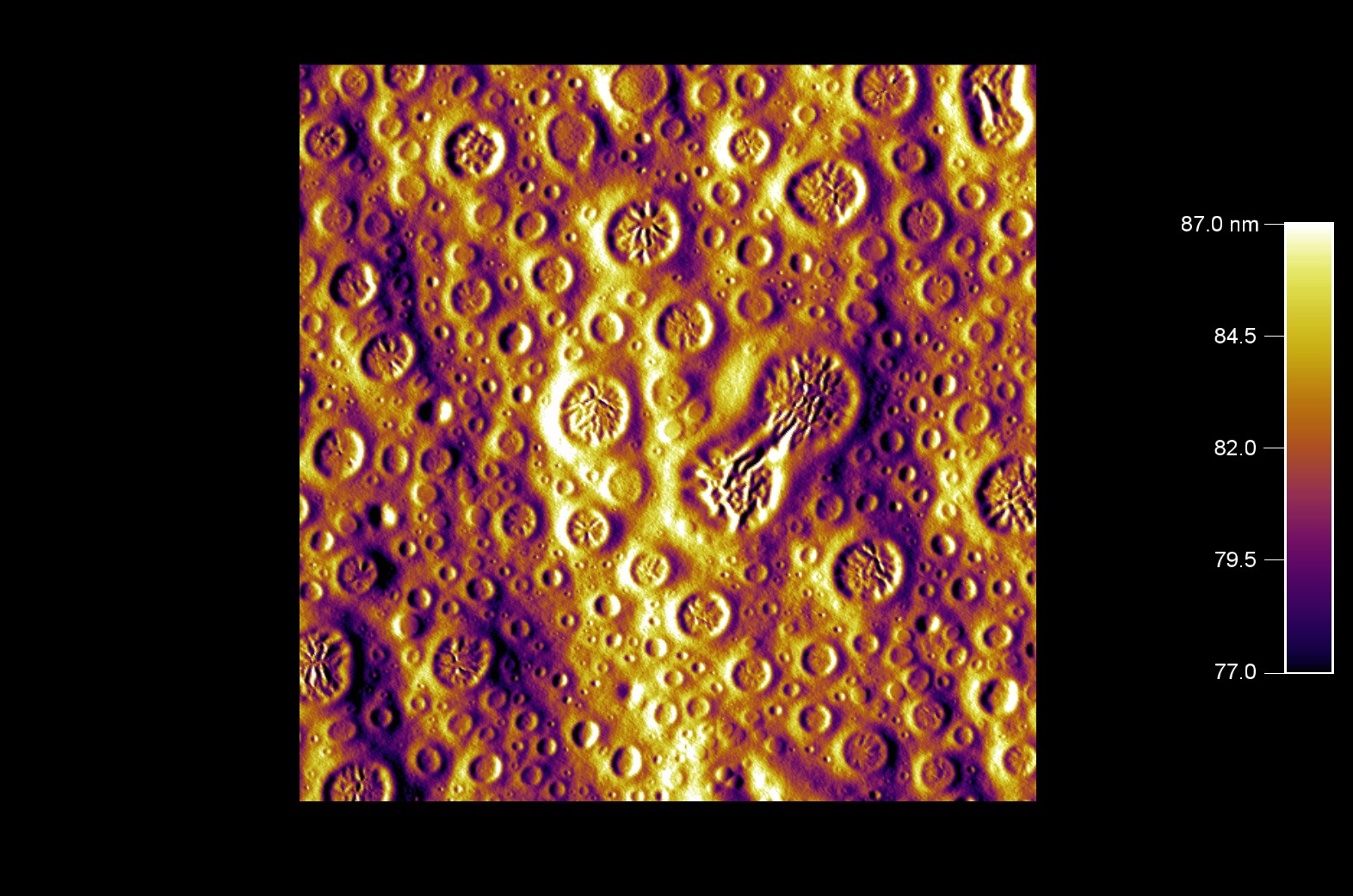
スパッタリング前の表面上の汚染物質が、典型的なスパッタ コーンの形成を引き起こす。
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 1.5 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
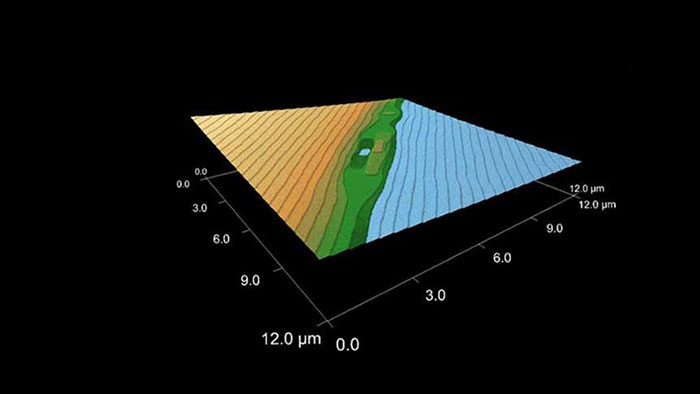
1400℃でアニールした後のサファイア結晶。原子ステップと時折欠陥のある清浄面を見ることができる。ステップの高さは約 3 Å 。
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ 12 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
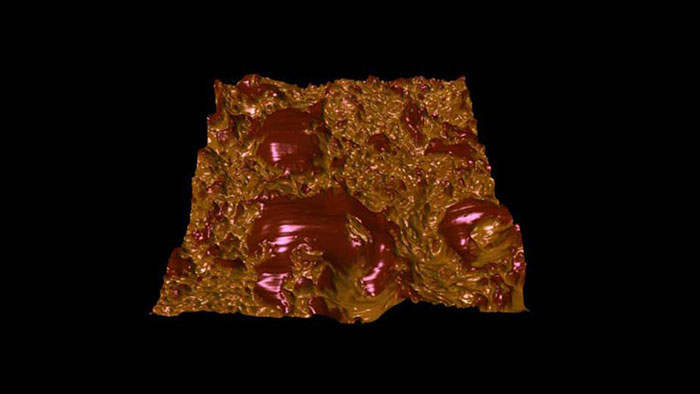
チョコレートは、主に細かく結晶化した連続した脂肪脂質マトリックス (ココアバター) からなり、その中にココアパウダーと砂糖粒子が分散した複雑な物質である。時間の経過とともに、脂質の結晶が結合してミクロンスケールの大きな結晶を形成する傾向があり、チョコレートの食感や味に大きな影響を与えている。この画像は、熟成させた市販のダーク チョコレート。表面形状を 3Dで表示し 、位相像をカラーデータとしてオーバーレイした。組成の違いを強調表示している (暗い部分は成長するココアバターの結晶)。
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 15 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
鞭毛を持つ大腸菌
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 6 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA

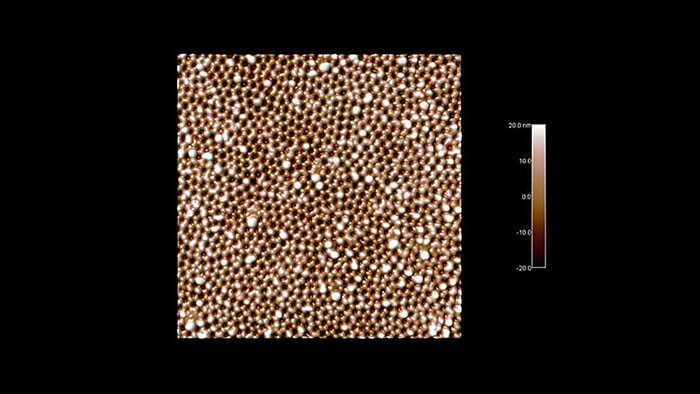
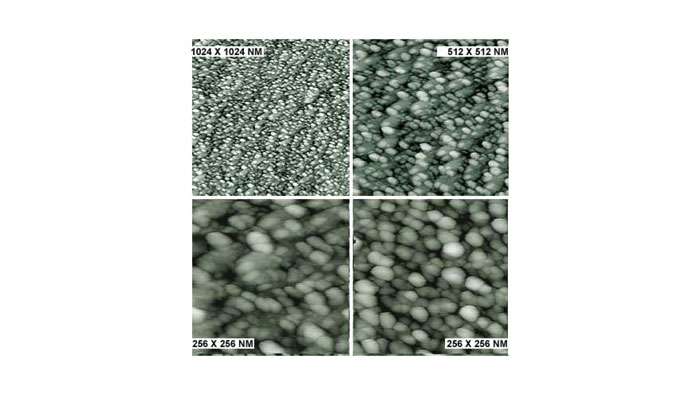
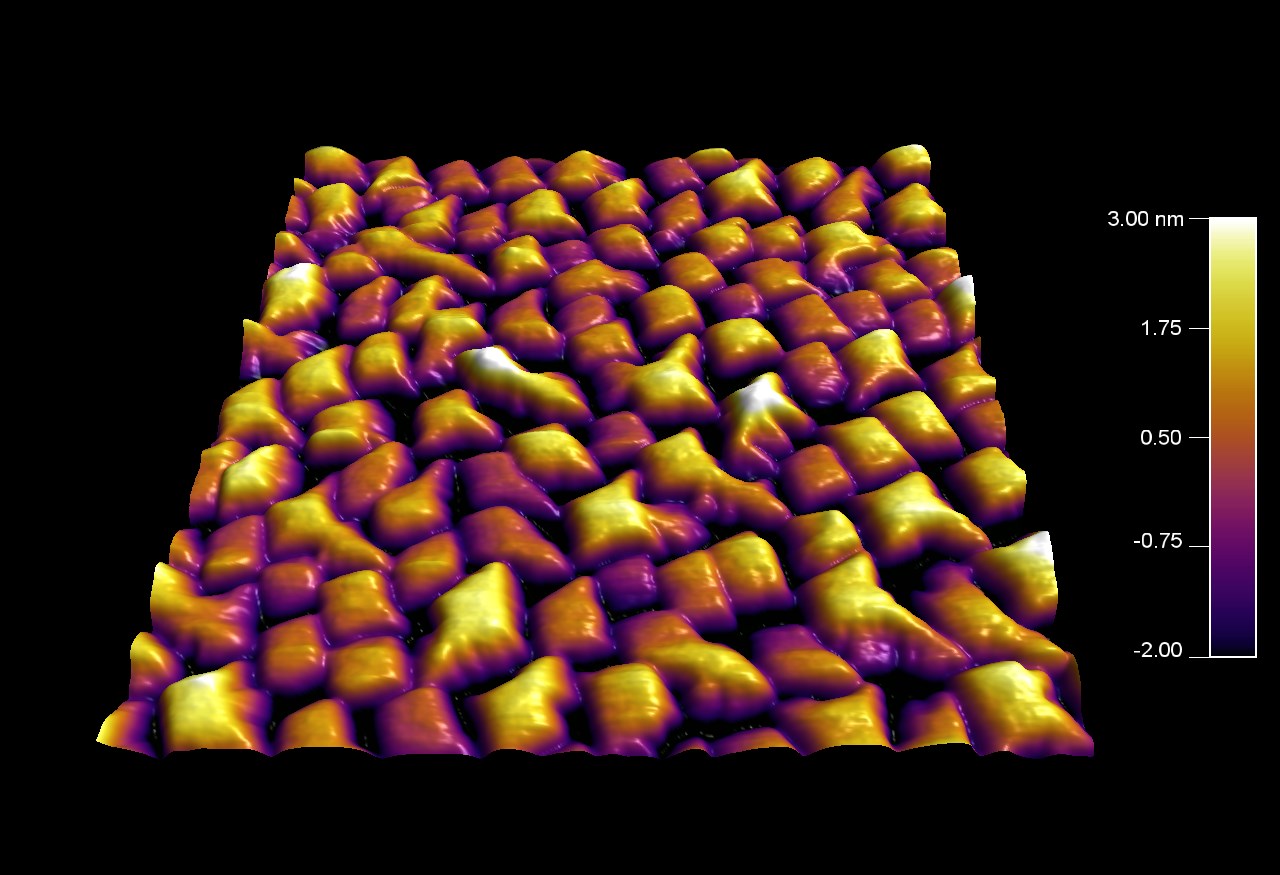
高配向熱分解黒鉛 (HOPG) サンプル
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 1024 nmスキャン
Image courtesy of Albert Lin, Angsnanotek Co., Ltd., Taiwan
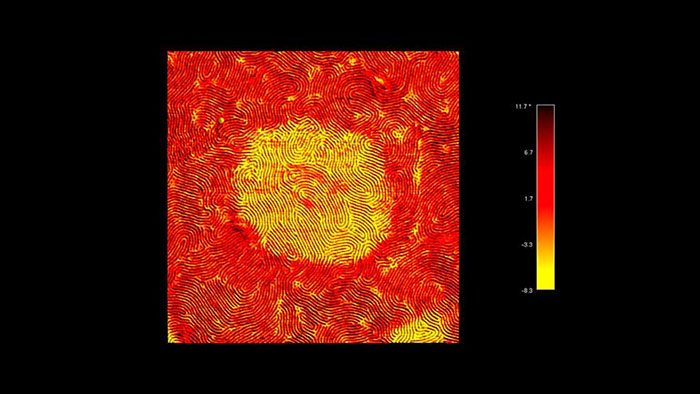
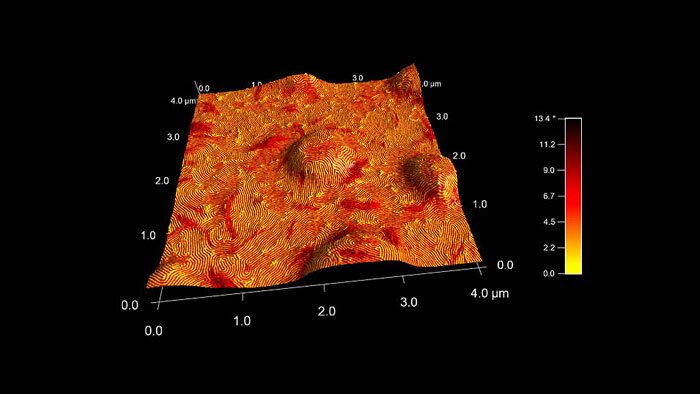
スチレン-エチレン-ブチレン-スチレン (SEBS) トリブロック共重合体の位相像
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 3 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
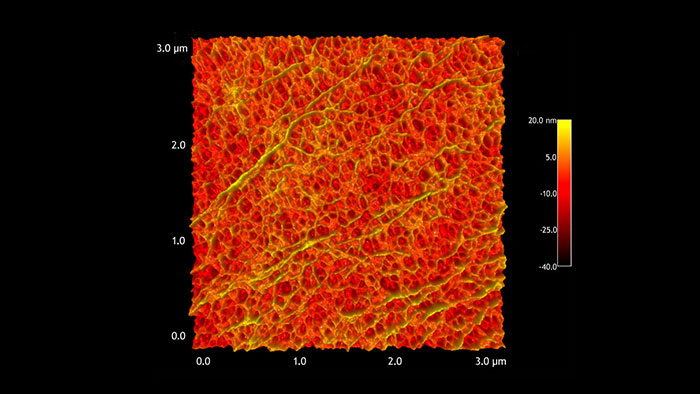
アルマイトの多孔質表面
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 3 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
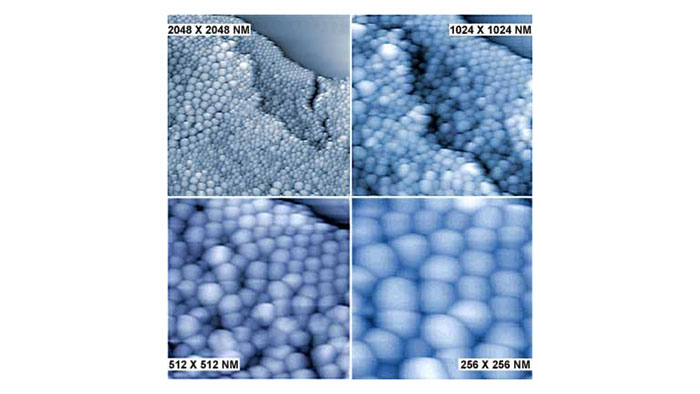
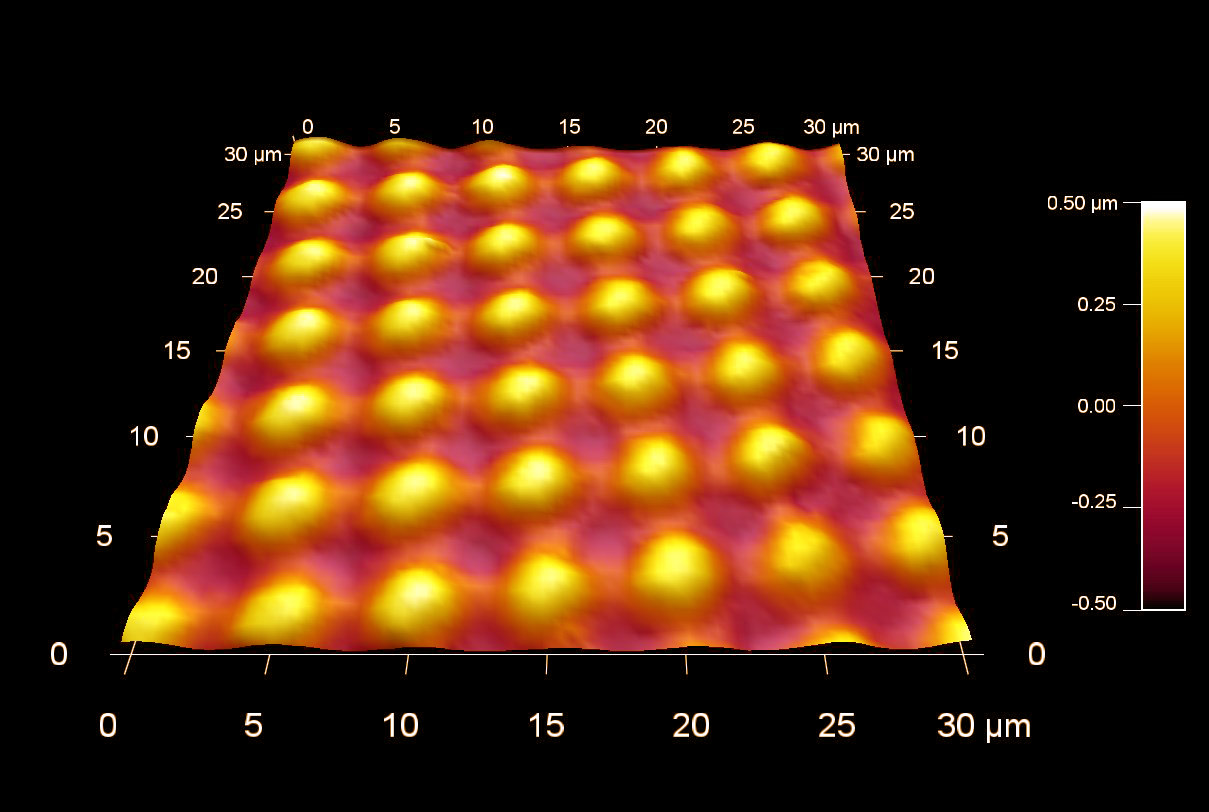
Zinc oxide酸化亜鉛ナノ粒子 (20~50nm)
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 2048, 1024, 512, 256nmスキャン
Image courtesy of Albert Lin, Angsnanotek Co., Ltd., Taiwan
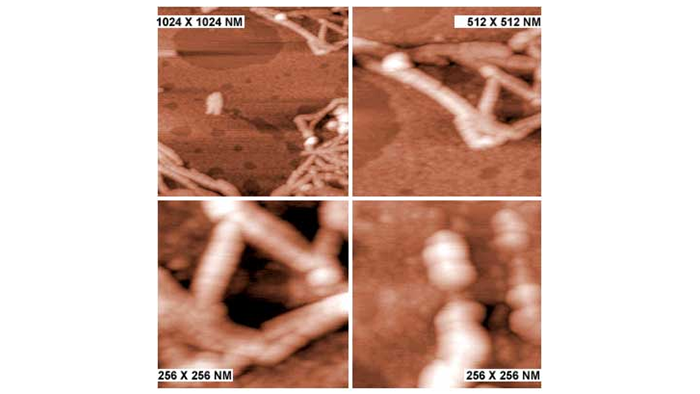
アミロイドファイバー (4~8nm)
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 1024nm から256 nmスキャンまで拡大
Image courtesy of Albert Lin, Angsnanotek Co., Ltd., Taiwan
ブレンドされた2つの生体高分子と相溶化剤
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ 2 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Nagoya Municipal Industrial Research Institute Japan
ポリオキシメチレン (POM) のらせん転位
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 3 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Jeff Kalish, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
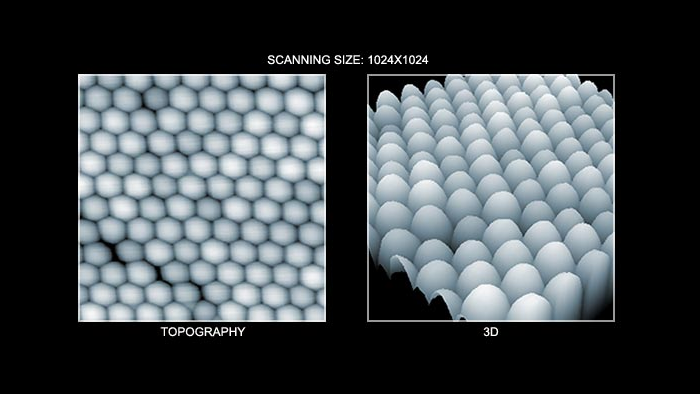
ナノパーティクルの形状 (左図) とその3D表示(右図)
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ 1024 nmスキャン
Image courtesy of Albert Lin Angsnanotek Co., Ltd., Taiwan
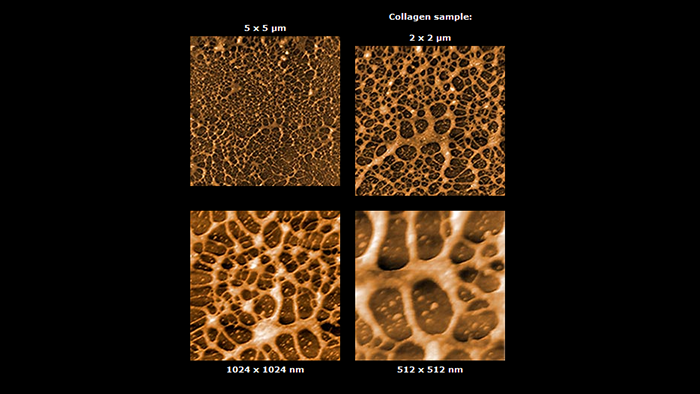
コラーゲンの表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ. 5000, 2000, 1024 , 512 nmスキャン
Image courtesy of Albert Lin, Angsnanotek Co., Ltd., Taiwan
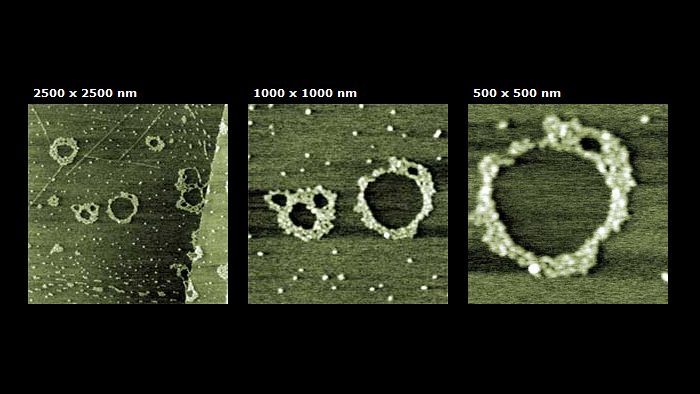
X-174 RF ラムダ DNA
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ. 2500, 1000 ,500 nmスキャン
Image courtesy of Albert Lin, Angsnanotek Co., Ltd., Taiwan
ポリスチレン中のさまざまなポルフィリン凝集体のインプリント
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 5 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Walter Smith, Haverford College, Haverford, USA
ZnO パーティクル (<10nm)
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ 1024, 512, 256 , 256nmスキャン
Image courtesy of Albert Lin, Angsnanotek Co., Ltd., Taiwan
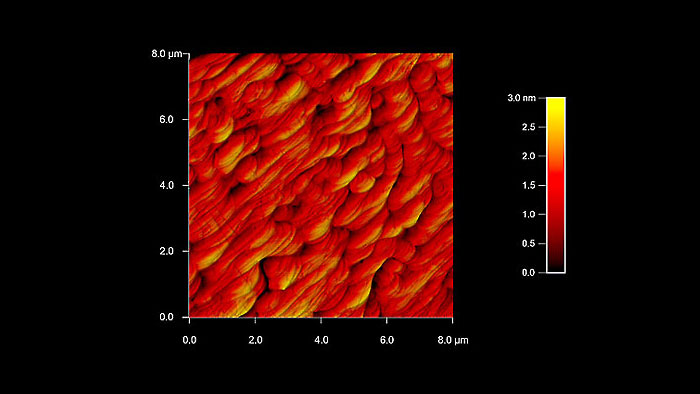
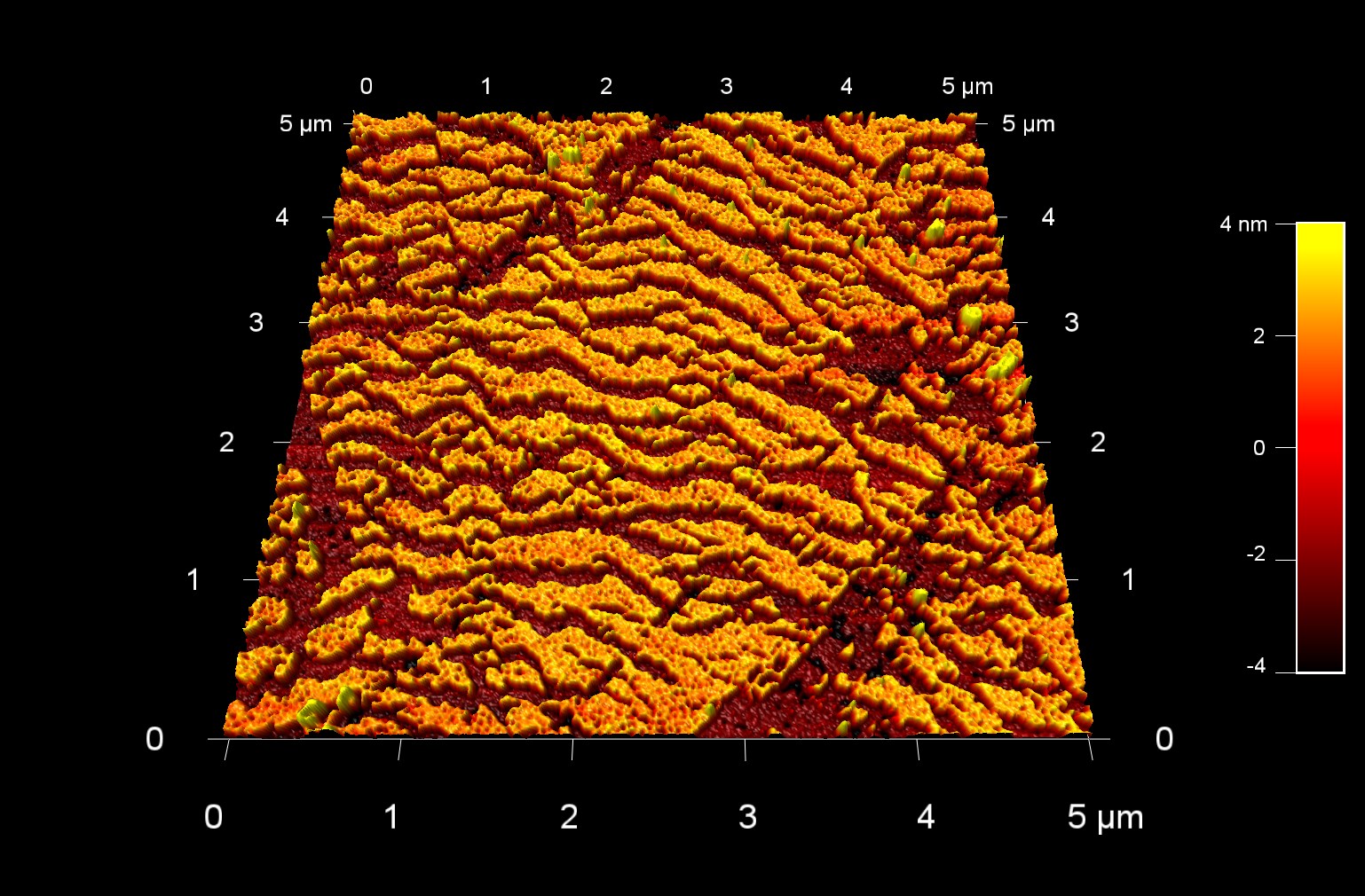
二軸延伸ポリプロピレン (BOPP)の表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ 3 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
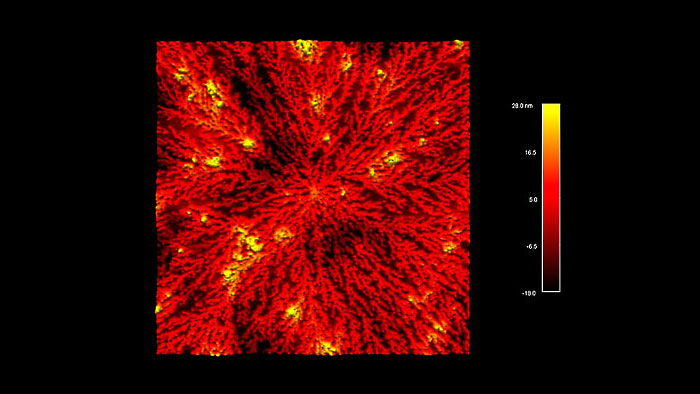
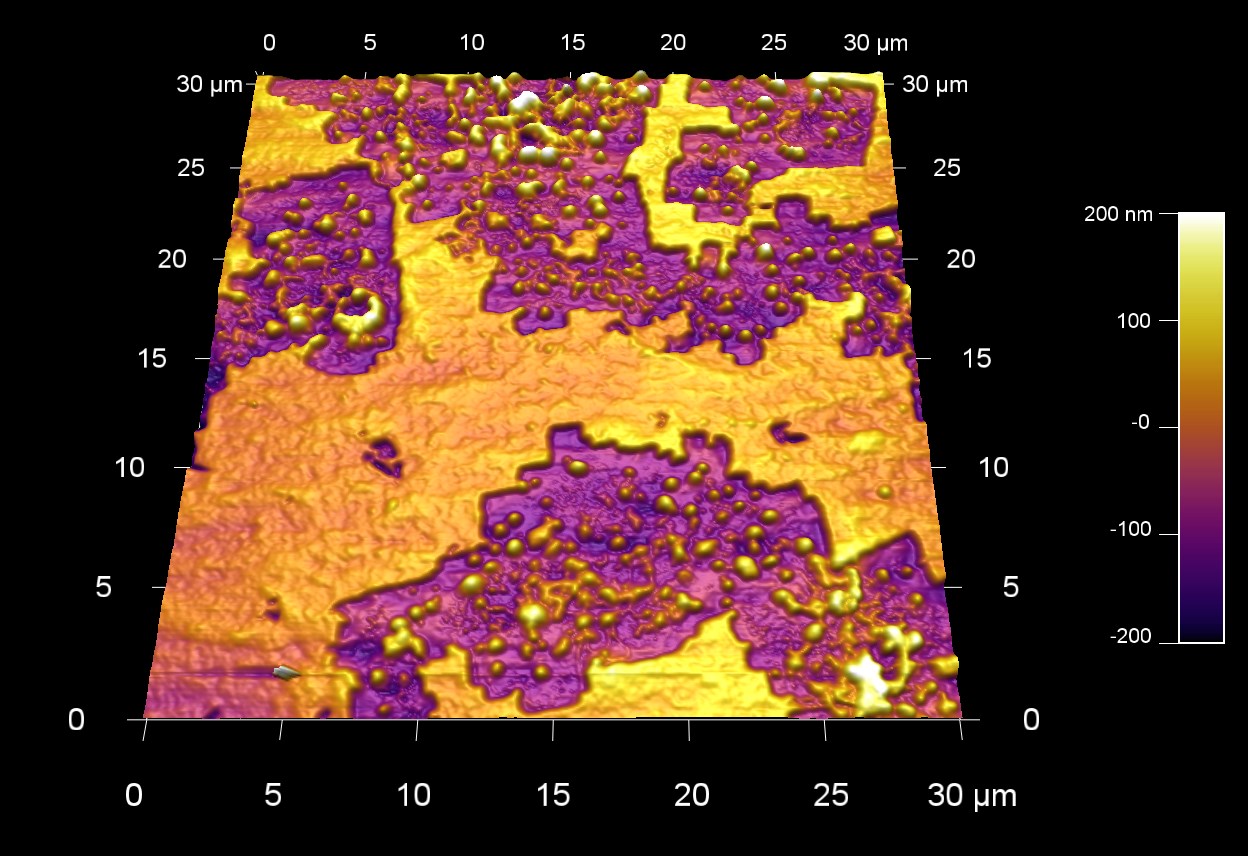
樹状成長した白金ナノクラスター
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 7 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
窒化クロム粒子
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 2 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
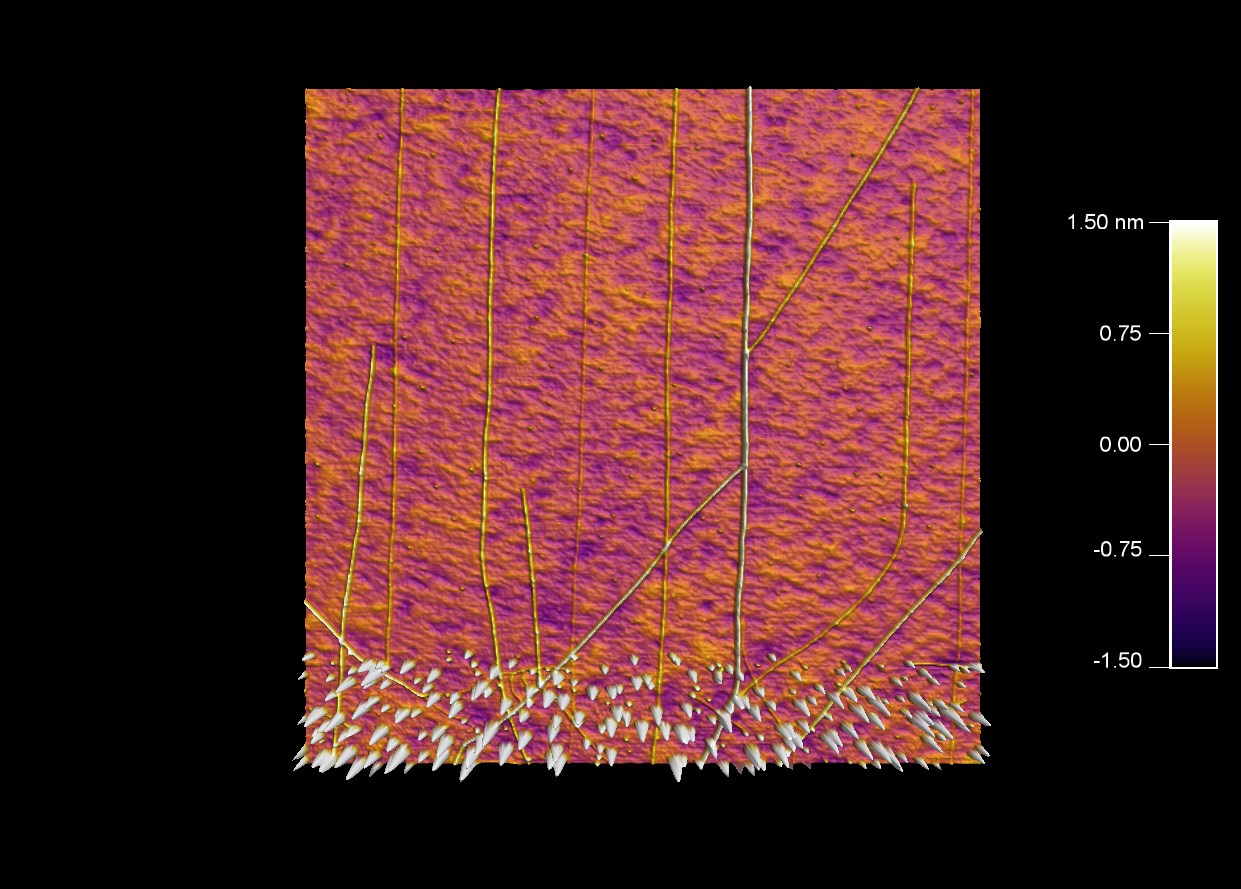
触媒粒子の列から延びるカーボンナノチューブ
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 5 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
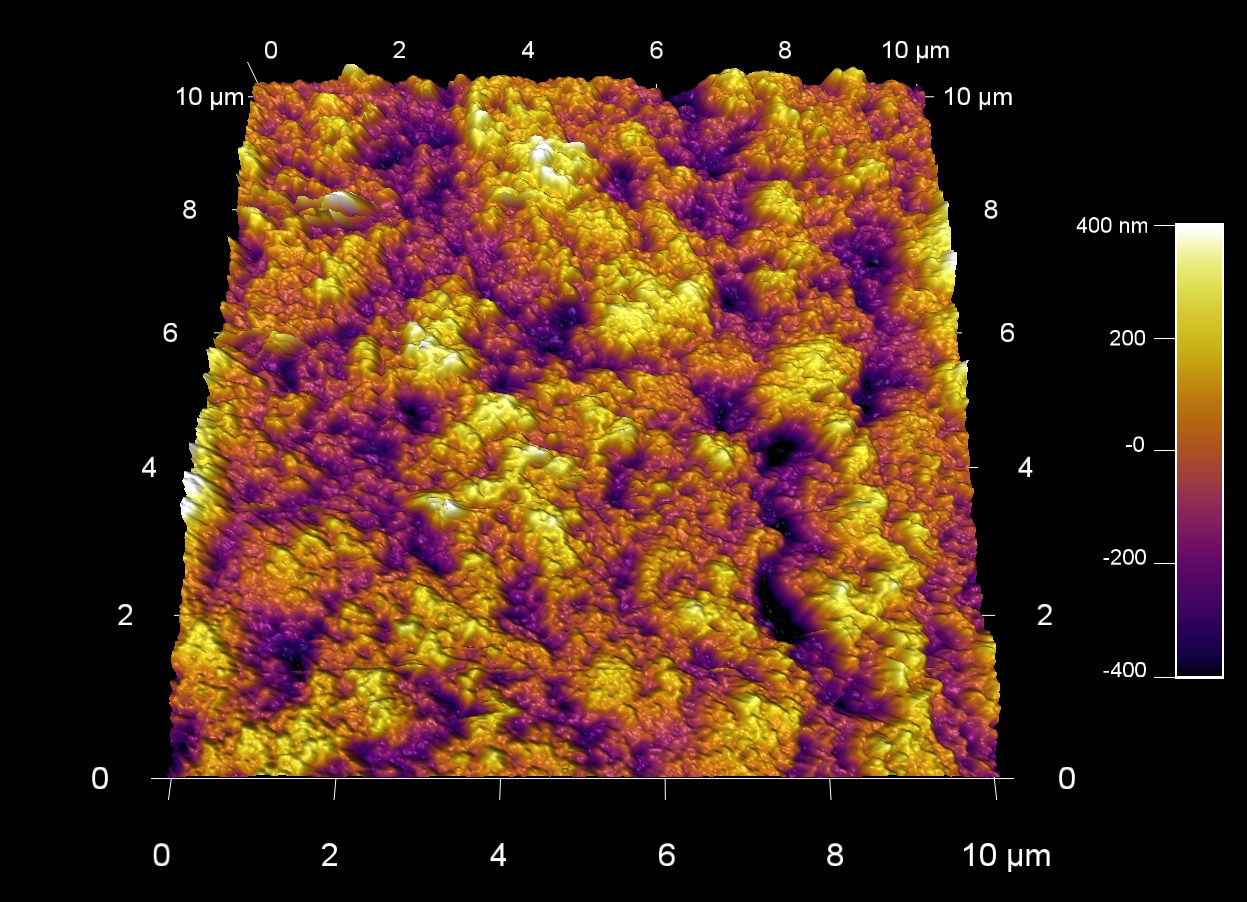
速乾性の白糊
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, アンプリチュード像 10umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
ガチョウの羽根ペンの表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ, 10 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
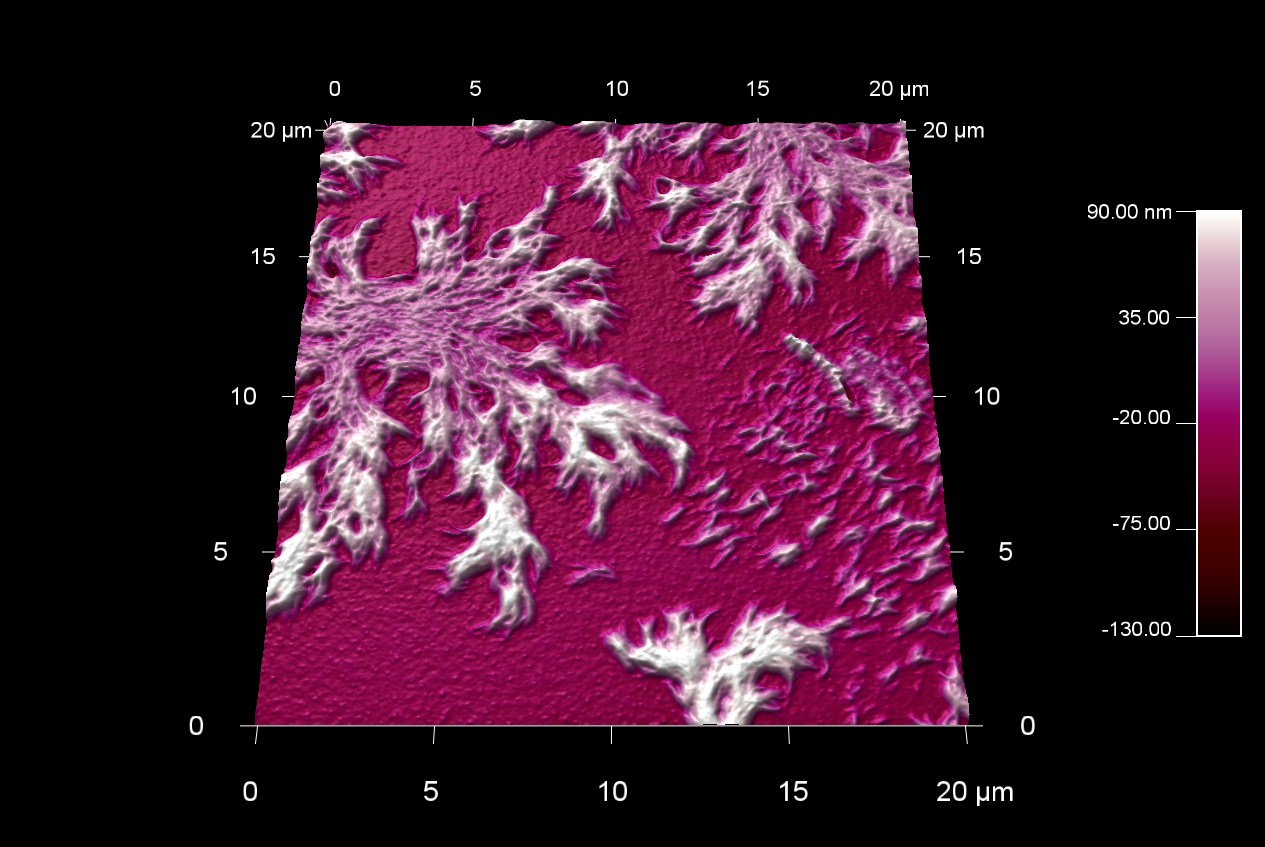
HDI ポリマーの樹状成長
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ20 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
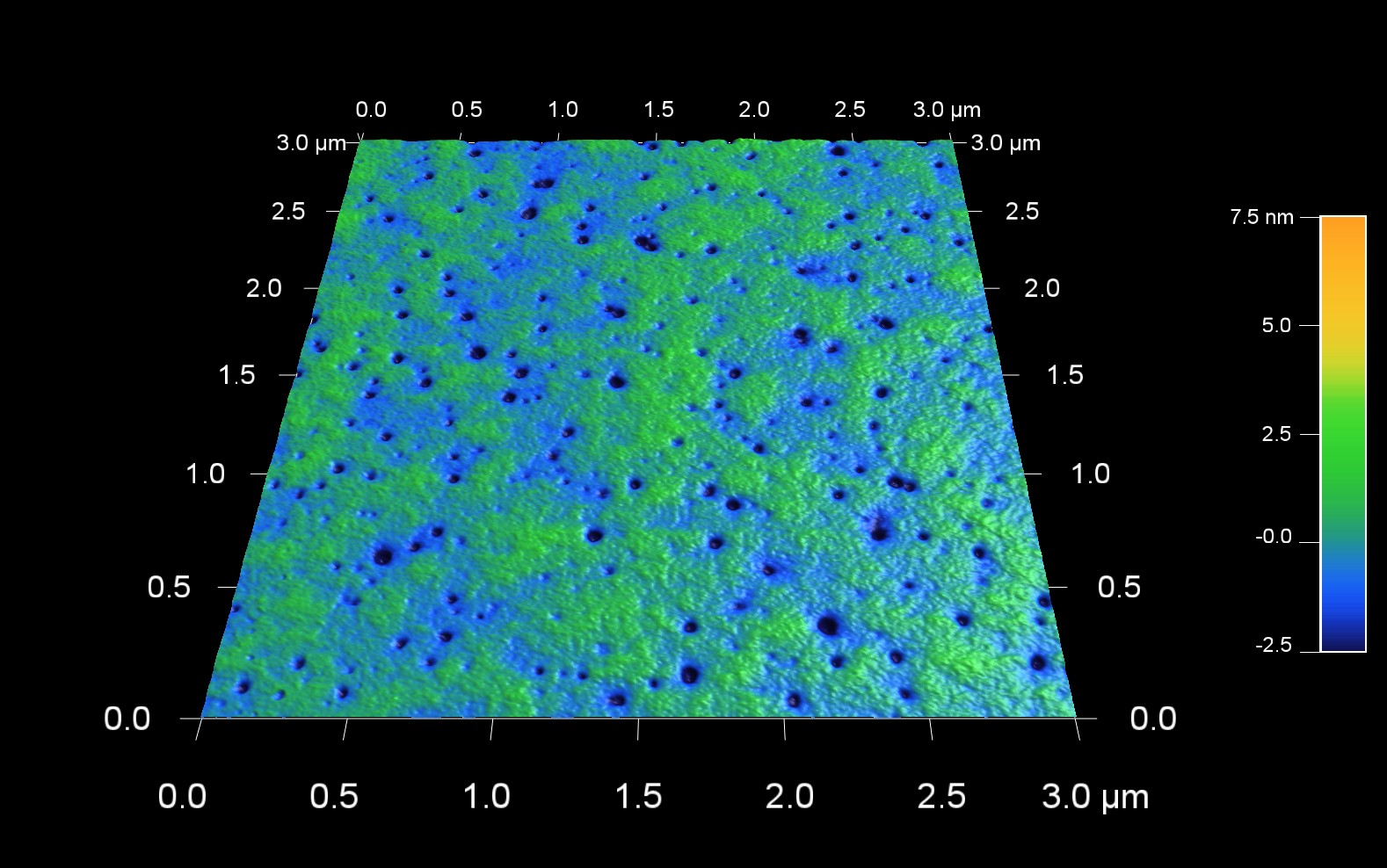
光沢紙の表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 3 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
ポリスチレンフォームの表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 30 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
ゴマの表面
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ 90umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
超疎水性表面
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ 90 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
破断した金パラジウム薄膜
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ 5umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
二次元光学グレーティング プラスティック製
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ 30 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
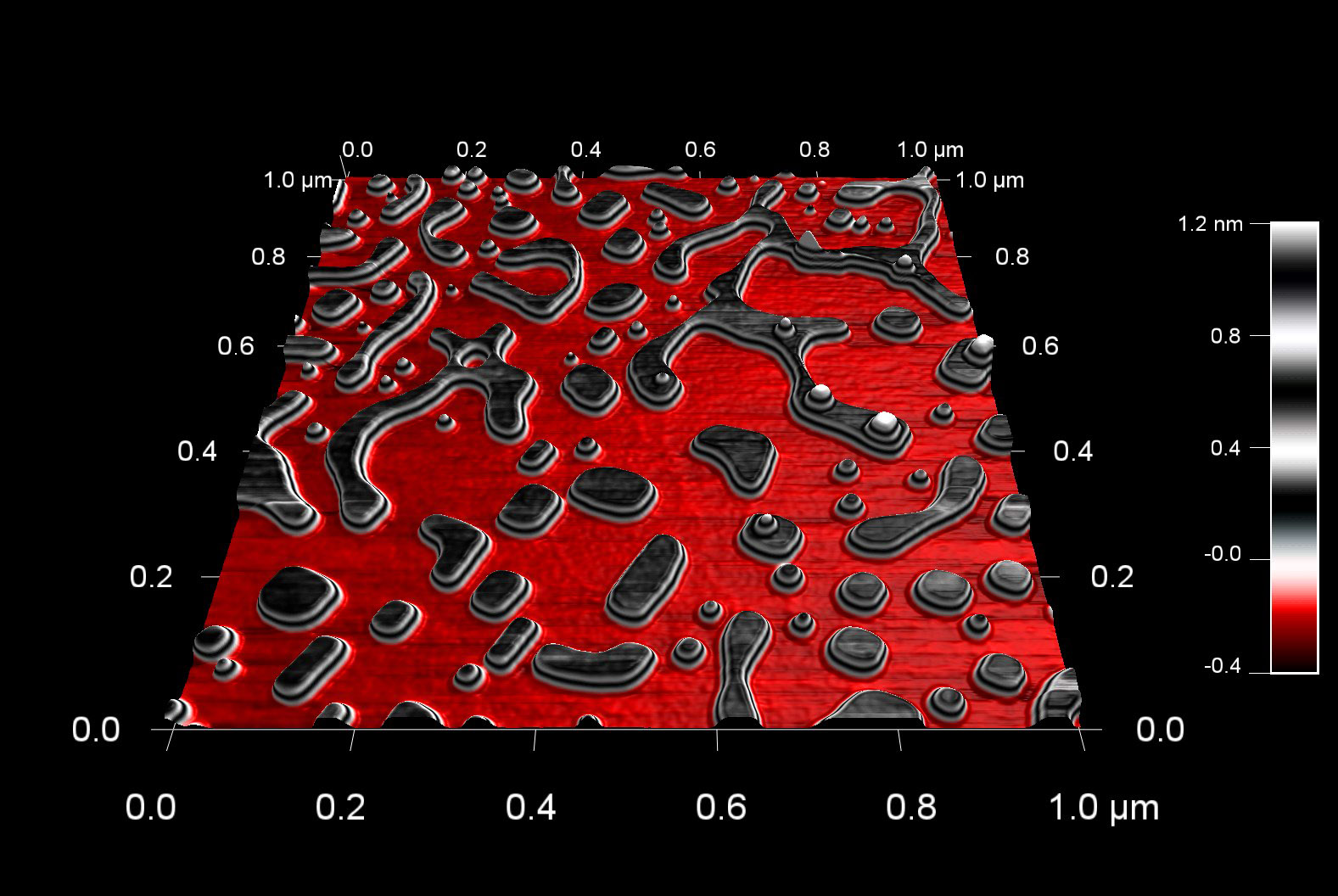
水でエッチングした石膏結晶
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 1 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
合成オパールの表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 9 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
パセリの種の表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ 30umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
ポリスチレンとポリカプロラクトンのブレンドポリマー
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ, 10 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
ローズマリーの葉の表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ 12 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
セージの種子の表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 80 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
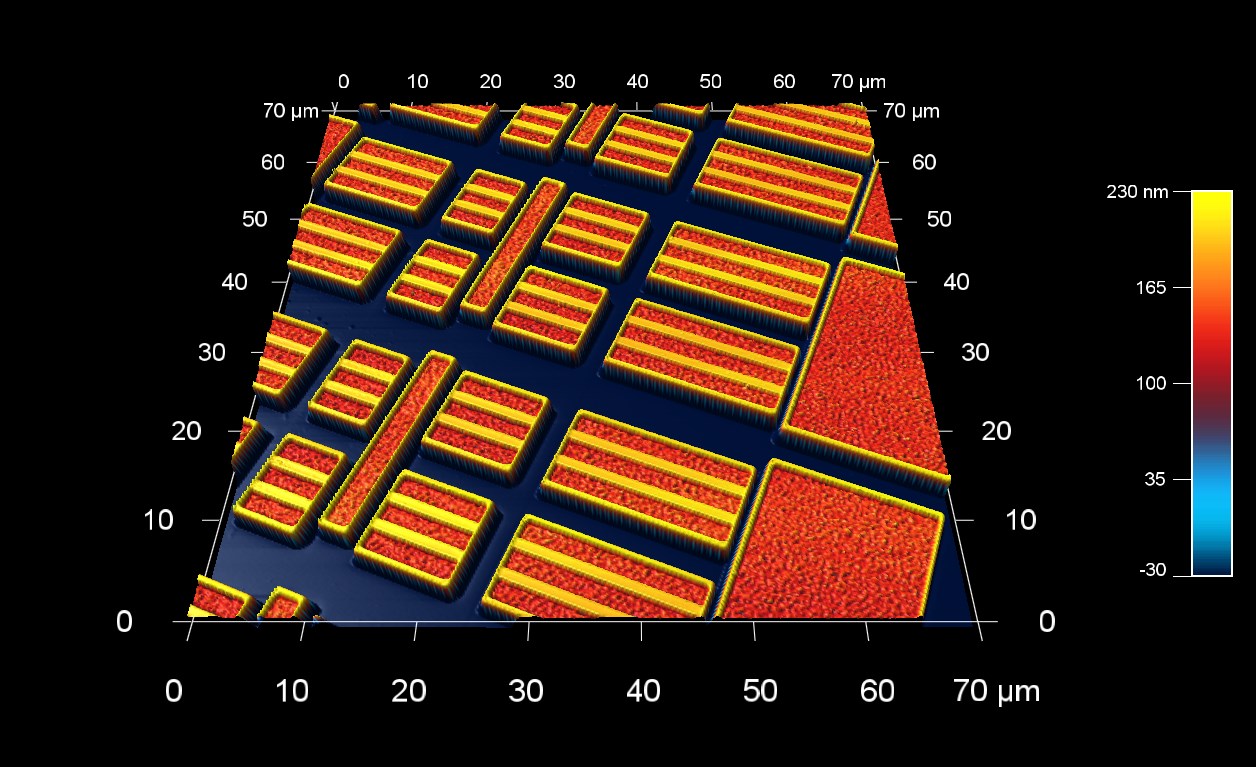
SRAM メモリの表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 70 μmスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
タイムの種子の表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ, 90 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
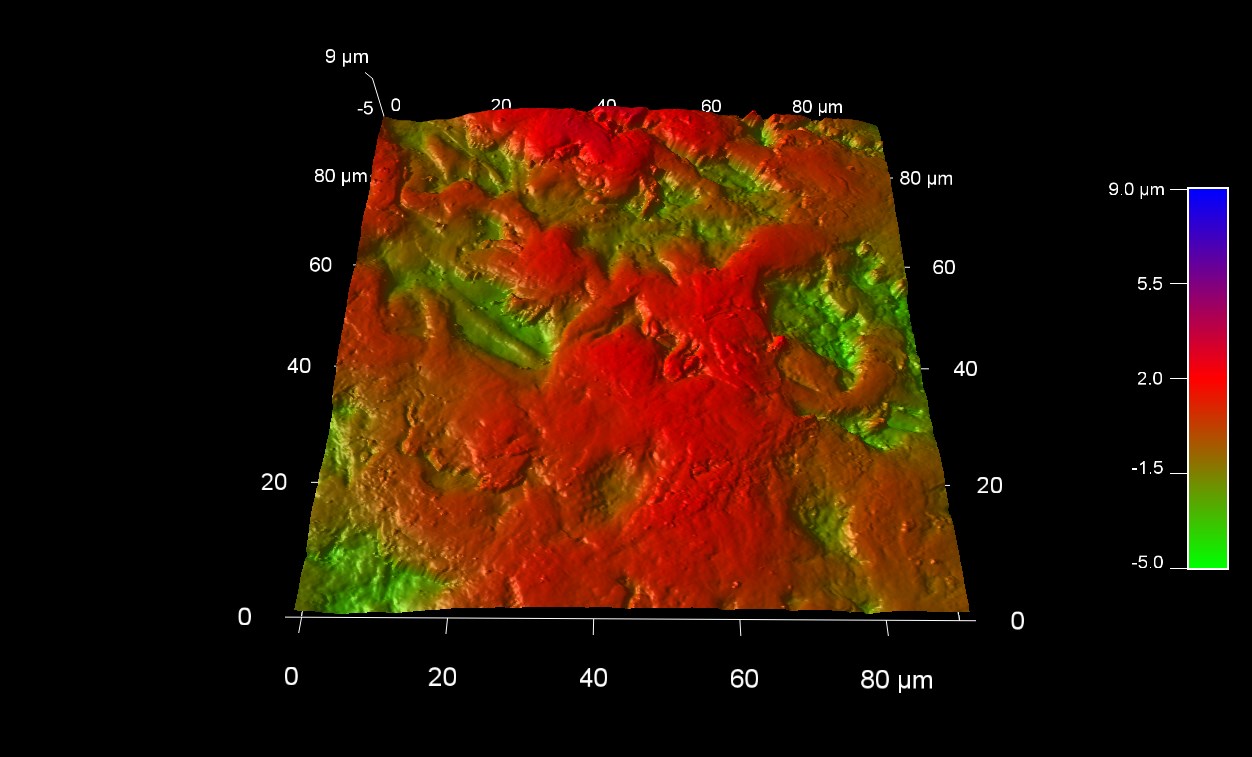
トマトの種子の表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 90 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
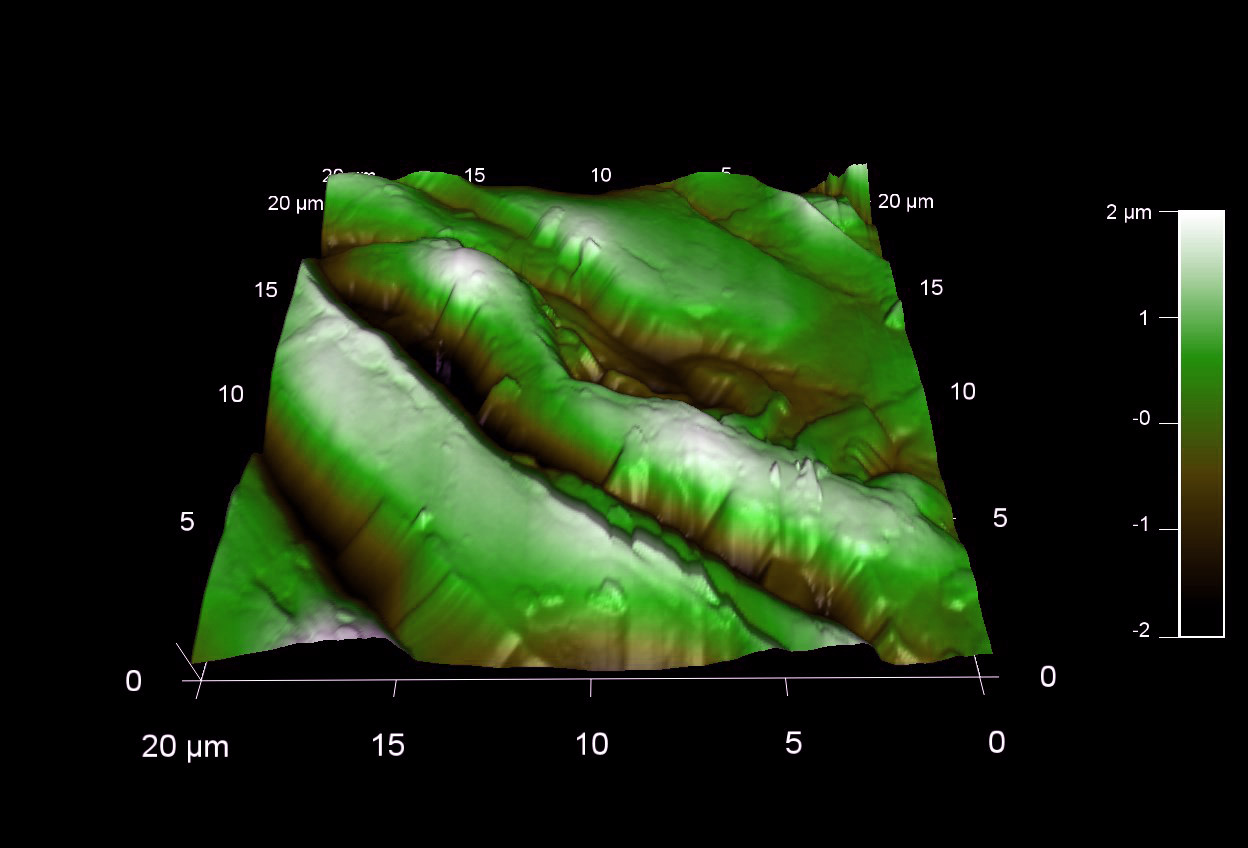
ズッキーニの種子の表面形状
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 20 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
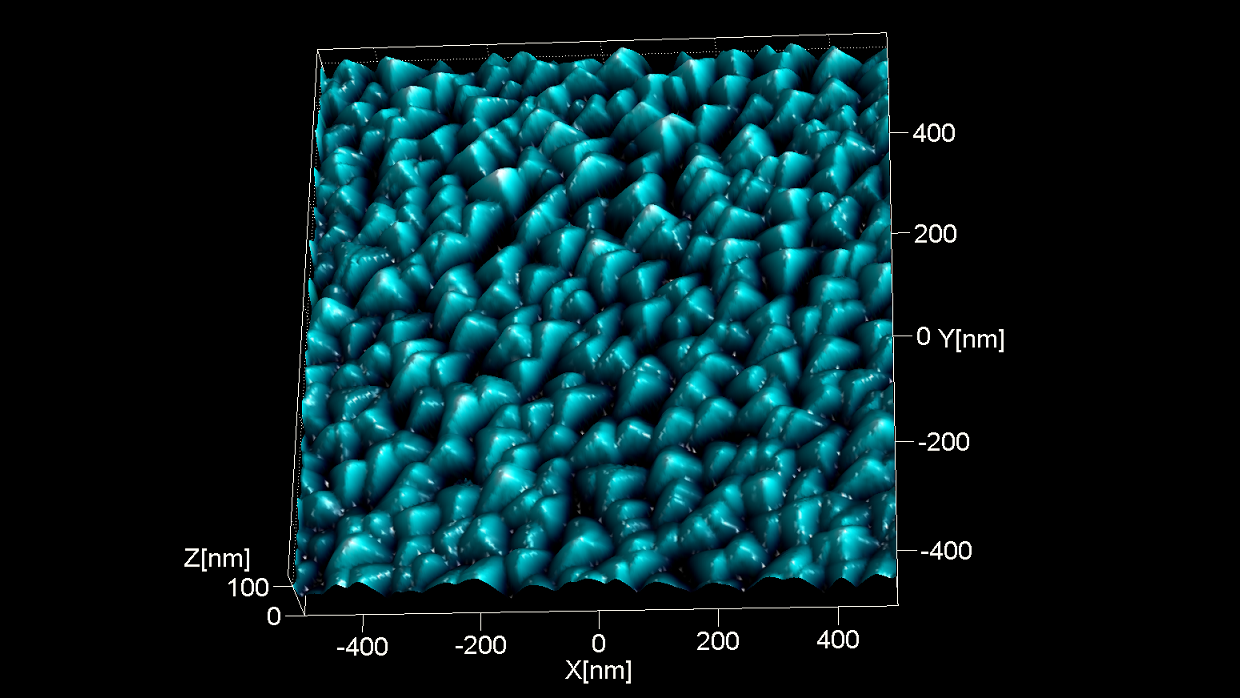
TipCheck は、BudgetSensors AFM プローブ 探針評価サンプルです。鋭いピラミッド構造により、探針先端の頂点の反転イメージを撮像できます。
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 1 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Dr. Yordan Stefanov, Innovative Solutions Bulgaria
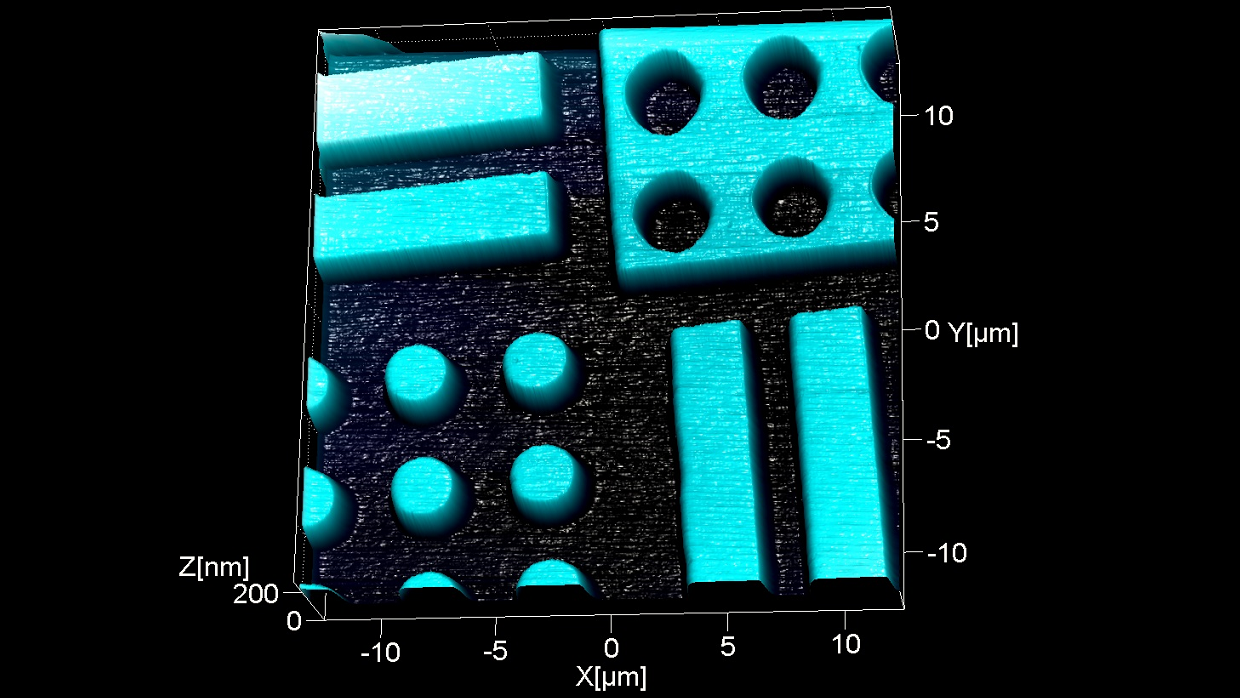
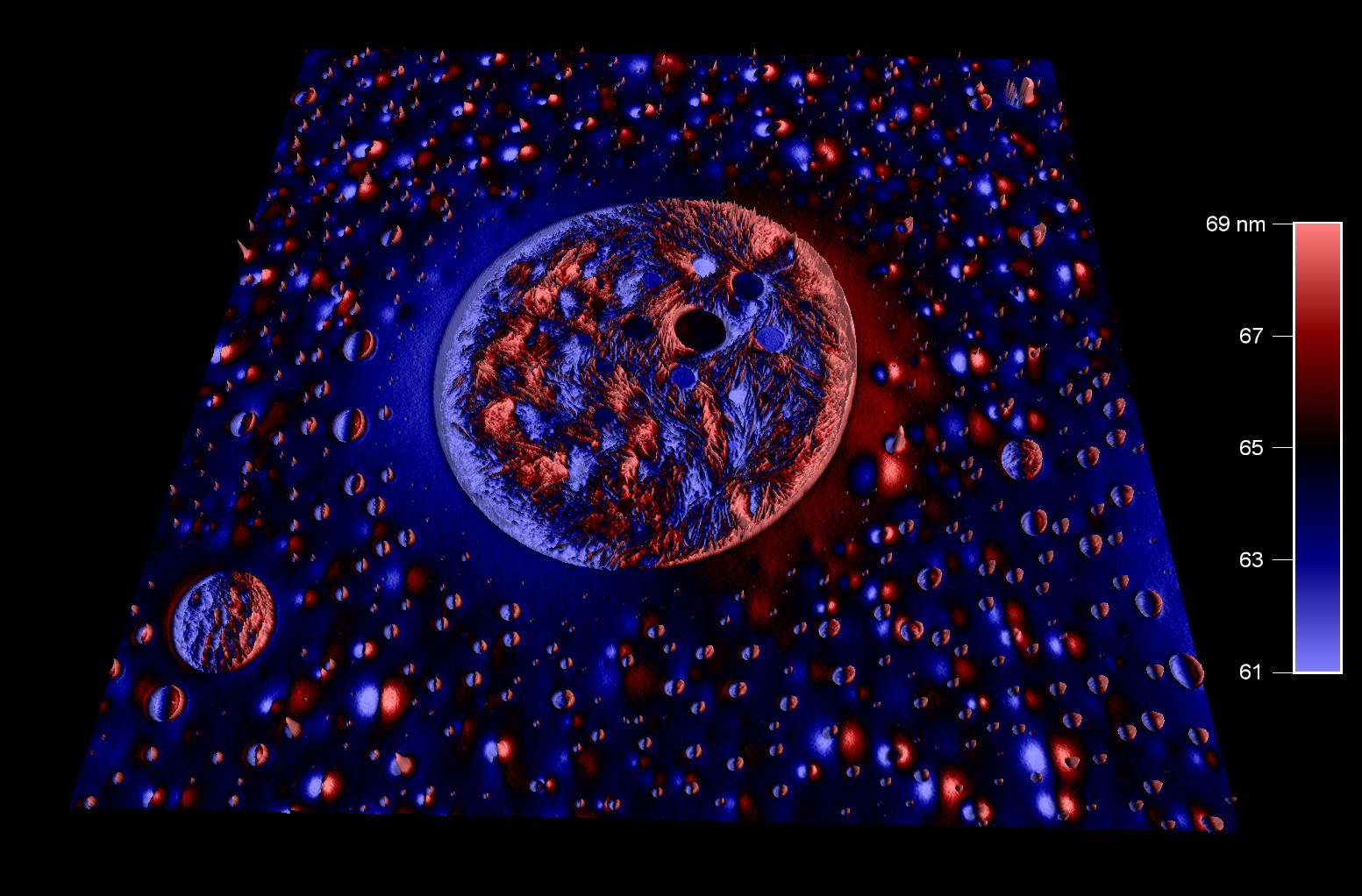
BudgetSensors の高さ校正リファレンス HS-100MG の中央部分の形状像 (公称ステップ高さ 100 nm)。 HS-100MG は、大面積スキャナの X-Y キャリブレーションに使用できます。アレイ構造により、X 軸と Y 軸のキャリブレーションを行うためにサンプルを回転したり再アライメントすることなく、AFM システムをキャリブレーションすることができます。
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 25umスキャン
Image courtesy of Dr. Yordan Stefanov, Innovative Solutions Bulgaria
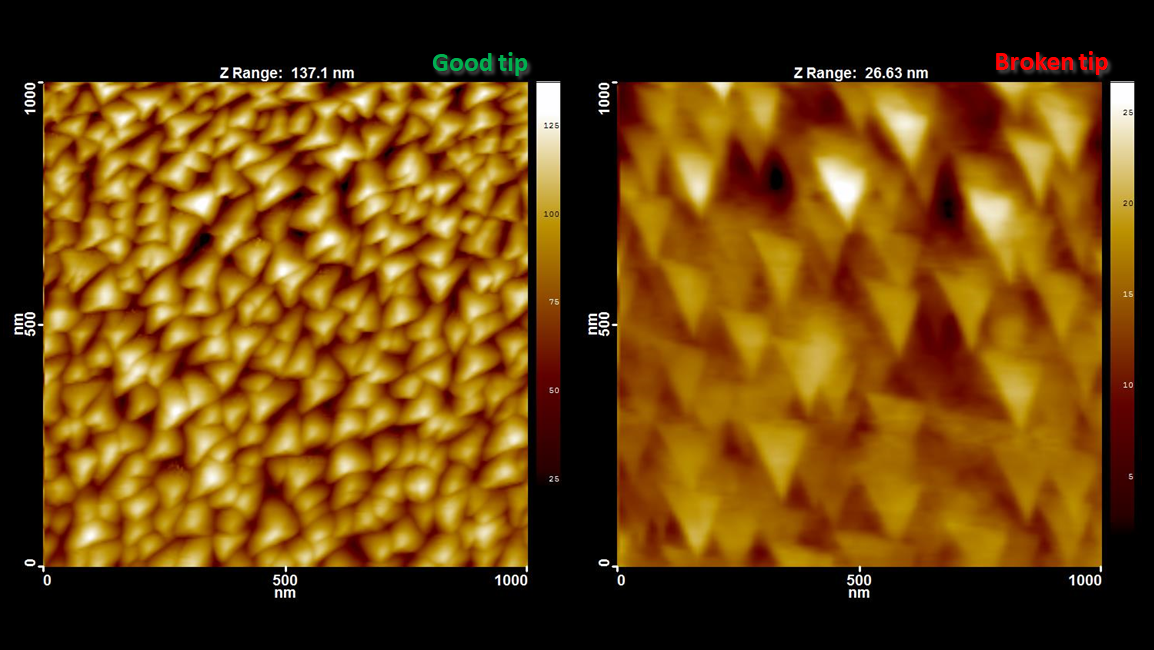
小さな形状を正確にイメージングするには、AFM探針の曲率半径が一般的な形状サイズよりも十分に小さい必要があります。逆に、探針が測定対象よりもはるかに大きい場合、測定結果は探針先端自体の像になります。 左図は、新しい先端が鋭いプローブを使用しタッピング モード スキャンした例で、TipCheck のピラミッド構造がよくわかります。右図は、ダメージを受けた探針を使用し TipCheckを測定した例です。プローブの不適切な取り扱いによって探針先端が壊れていることがはっきりとわかります。
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ, 1 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Dr. Yordan Stefanov, Innovative Solutions Bulgaria
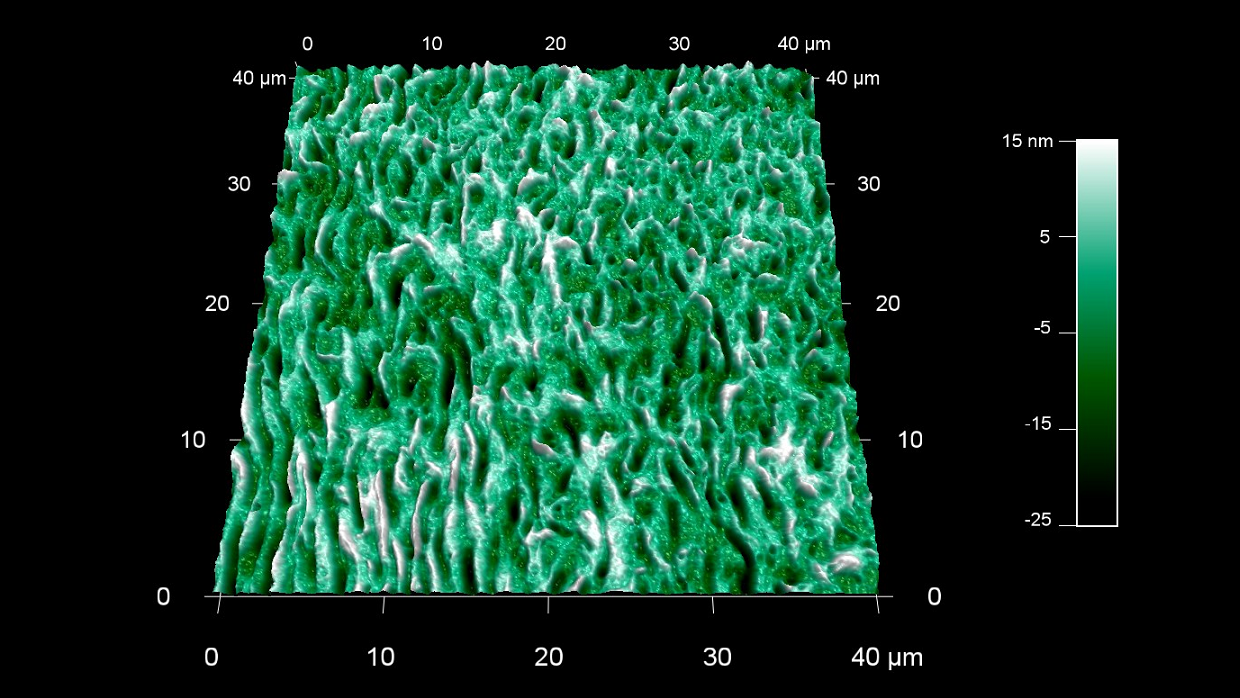
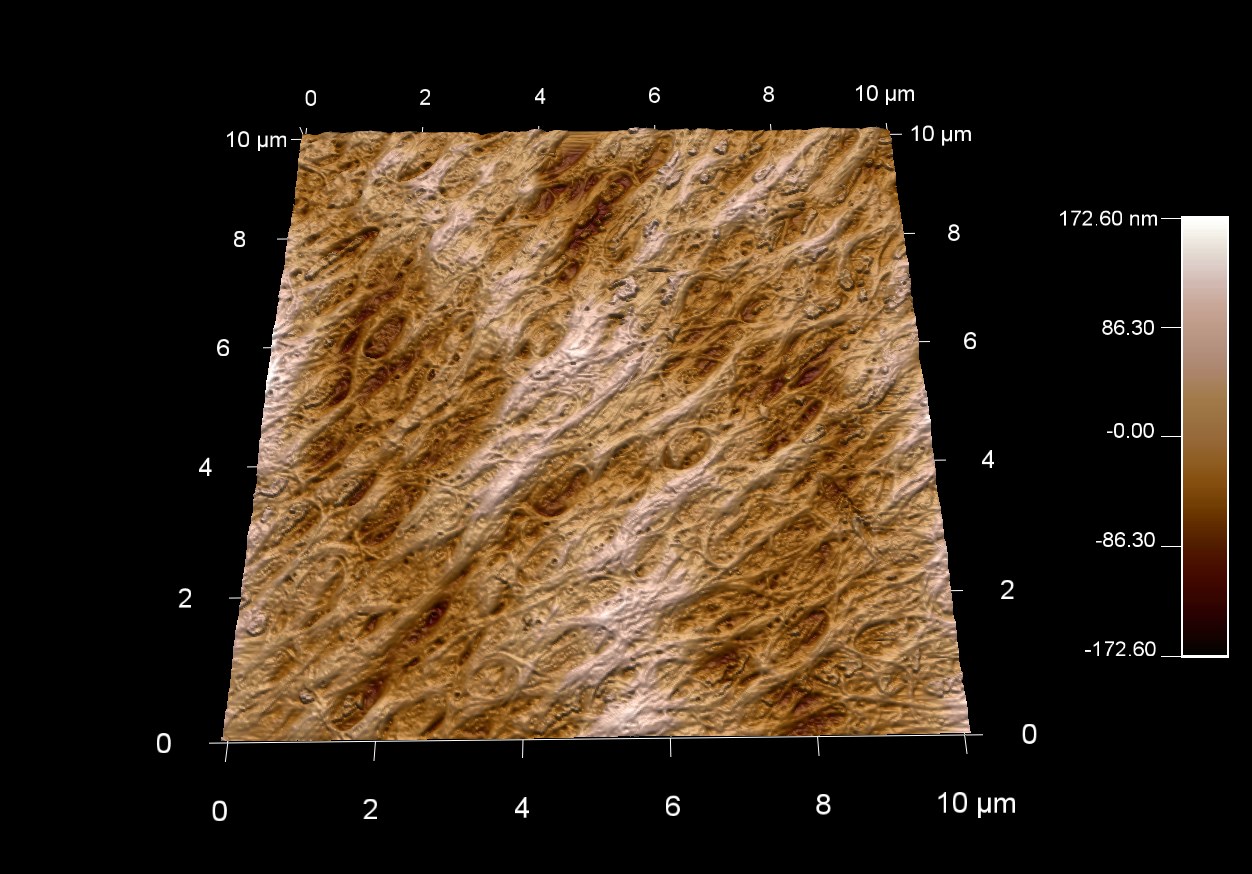
コラーゲンは私たちの体内で最も豊富なタンパク質であり、総タンパク量の約30%を占めていることをご存知ですか?
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM プローブ 40 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
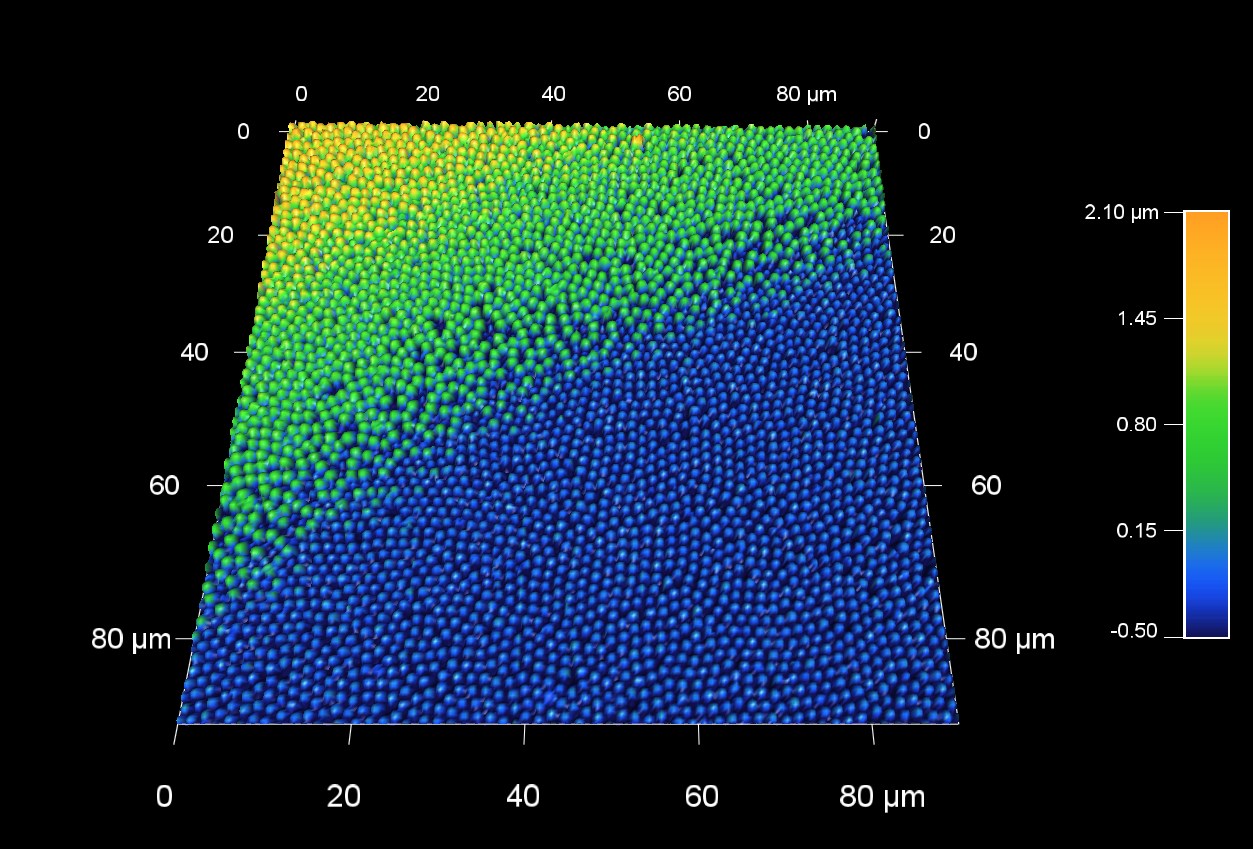
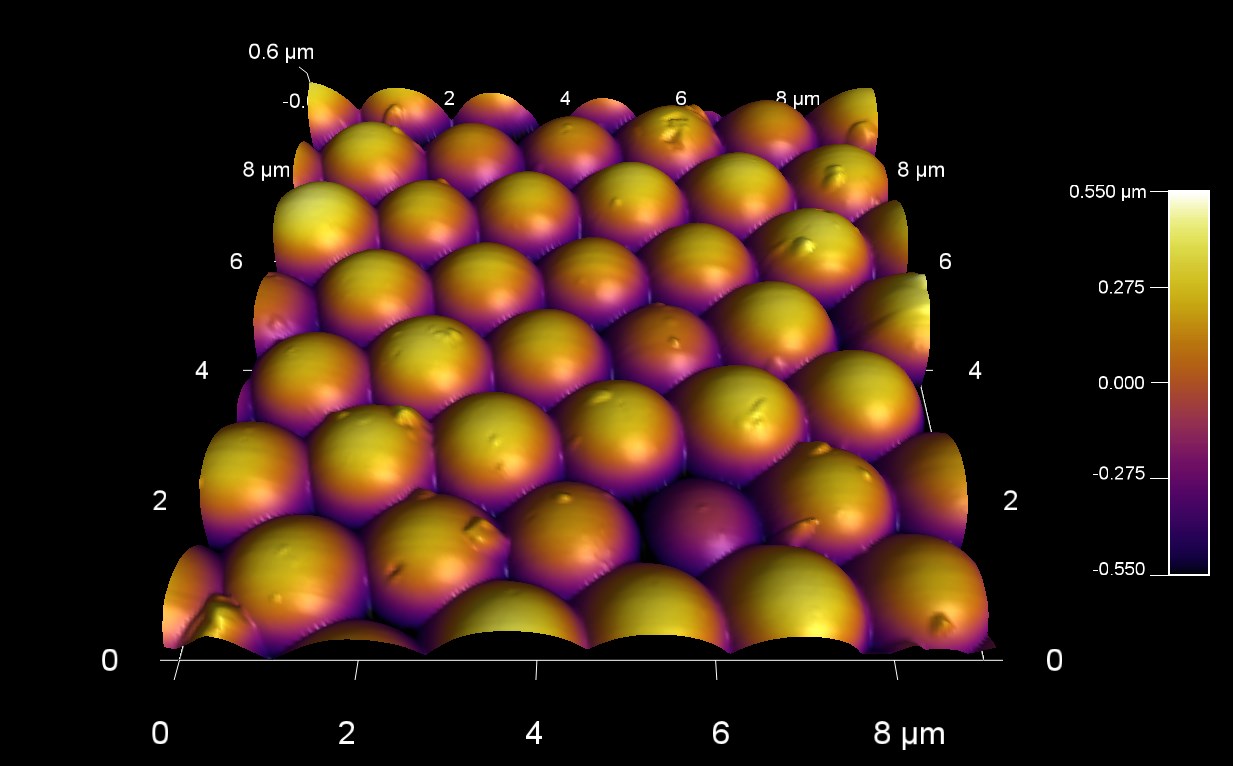
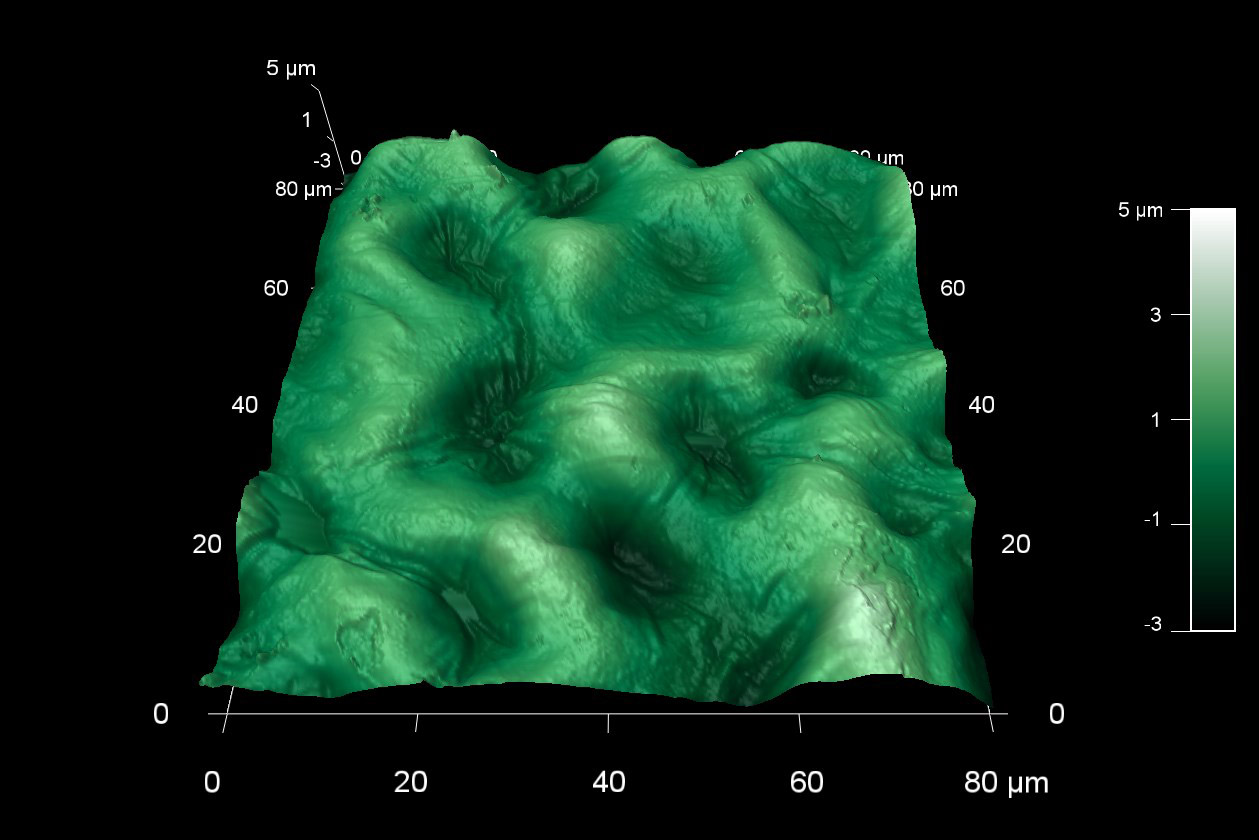
希少なオパールは、数百ナノメートルのサイズの密集したシリカ球で構成されている。オパールの美しい色は、光の回折と干渉によって作られている。この 90 um AFM スキャンは、ナノ球体で構成されているオパール表面の、2つの平面の境界部分を測定したものです。
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFM probe, 90 micron scan size
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
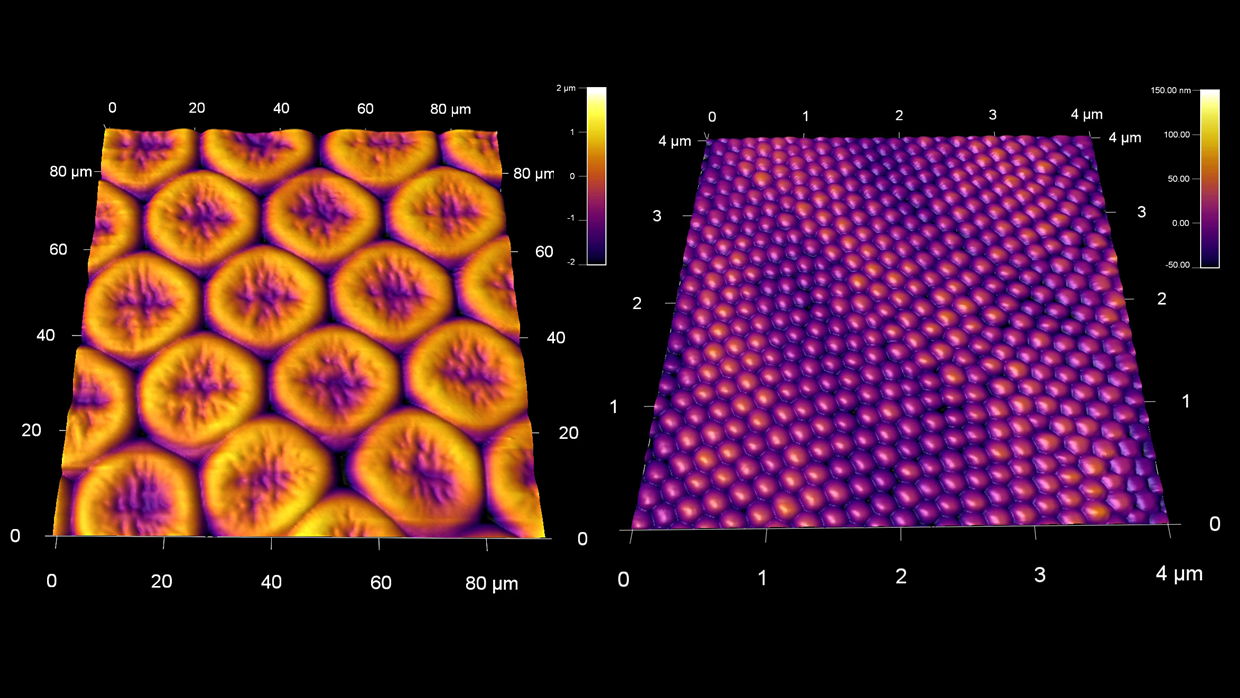
乾燥した蝶の複目の大規模構造(左)と面を覆う微細なナノ構造(右)
スキャン BudgetSensors Tap300Al-G AFMプローブ, 90umと 4 umスキャン
Image courtesy of Scott MacLaren, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA